Elimination of insulitis and augmentation of islet beta cell regeneration via induction of chimerism in overtly diabetic NOD mice
- PMID: 17267595
- PMCID: PMC1785362
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0611101104
Elimination of insulitis and augmentation of islet beta cell regeneration via induction of chimerism in overtly diabetic NOD mice
Abstract
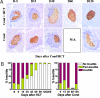
Type 1 diabetes in both humans and nonobese diabetic (NOD) mice results from autoreactive T cell destruction of insulin-producing beta cells. Cure of type 1 diabetes may require both reversal of autoimmunity and regeneration of beta cells. Induction of chimerism via allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation has been shown to reestablish tolerance in both prediabetic and diabetic NOD mice. However, it is unclear whether this therapy augments beta cell regeneration. Furthermore, this procedure usually requires total body irradiation conditioning of recipients. The toxicity of total body irradiation conditioning and potential for graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) limit the application of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for treating type 1 diabetes. Here we report that injection of donor bone marrow and CD4+ T cell-depleted spleen cells induced chimerism without causing GVHD in overtly diabetic NOD mice conditioned with anti-CD3/CD8 and that induction of chimerism in new-onset diabetic NOD mice led to elimination of insulitis, regeneration of host beta cells, and reversal of hyperglycemia. Therefore, this radiation-free GVHD preventive approach for induction of chimerism may represent a viable means for reversing type 1 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
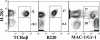
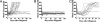
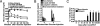
Similar articles
-
Donor CD8+ T cells facilitate induction of chimerism and tolerance without GVHD in autoimmune NOD mice conditioned with anti-CD3 mAb.Blood. 2005 Mar 1;105(5):2180-8. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-06-2411. Epub 2004 Sep 16. Blood. 2005. PMID: 15374883
-
Mixed chimerism and growth factors augment β cell regeneration and reverse late-stage type 1 diabetes.Sci Transl Med. 2012 May 9;4(133):133ra59. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3003835. Sci Transl Med. 2012. PMID: 22572882
-
Mixed allogeneic chimerism induced by a sublethal approach prevents autoimmune diabetes and reverses insulitis in nonobese diabetic (NOD) mice.J Immunol. 1996 Jan 1;156(1):380-8. J Immunol. 1996. PMID: 8598488
-
Recovery of the endogenous beta cell function in the NOD model of autoimmune diabetes.Stem Cells. 2003;21(4):377-88. doi: 10.1634/stemcells.21-4-377. Stem Cells. 2003. PMID: 12832692 Review.
-
Protective conditioning against GVHD and graft rejection after combined organ and hematopoietic cell transplantation.Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2008 Jan-Feb;40(1):48-54. doi: 10.1016/j.bcmd.2007.06.019. Epub 2007 Sep 10. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2008. PMID: 17827036 Review.
Cited by
-
Induction of chimerism permits low-dose islet grafts in the liver or pancreas to reverse refractory autoimmune diabetes.Diabetes. 2010 Sep;59(9):2228-36. doi: 10.2337/db10-0450. Epub 2010 Jun 8. Diabetes. 2010. PMID: 20530743 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary flavonol epicatechin prevents the onset of type 1 diabetes in nonobese diabetic mice.J Agric Food Chem. 2013 May 8;61(18):4303-9. doi: 10.1021/jf304915h. Epub 2013 Apr 30. J Agric Food Chem. 2013. PMID: 23578364 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial-encoded MOTS-c prevents pancreatic islet destruction in autoimmune diabetes.Cell Rep. 2021 Jul 27;36(4):109447. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109447. Cell Rep. 2021. PMID: 34320351 Free PMC article.
-
MHC-mismatched mixed chimerism augments thymic regulatory T-cell production and prevents relapse of EAE in mice.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Dec 29;112(52):15994-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1521157112. Epub 2015 Dec 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26647186 Free PMC article.
-
Stability of Chimerism in Non-Obese Diabetic Mice Achieved By Rapid T Cell Depletion Is Associated With High Levels of Donor Cells Very Early After Transplant.Front Immunol. 2018 Apr 24;9:837. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00837. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29740442 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Castano L, Eisenbarth GS. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:647–679. - PubMed
-
- Rossini AA. Diabetes. 2004;53:267–275. - PubMed
-
- Roep BO, Atkinson M, von Herrath M. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004;4:989–997. - PubMed
-
- Zucchelli S, Holler P, Yamagata T, Roy M, Benoist C, Mathis D. Immunity. 2005;22:385–396. - PubMed
-
- Pugliese A, Miceli D. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2002;18:13–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

