NF-kappa B prevents beta cell death and autoimmune diabetes in NOD mice
- PMID: 17267600
- PMCID: PMC1794308
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0610690104
NF-kappa B prevents beta cell death and autoimmune diabetes in NOD mice
Abstract
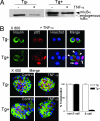
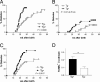
Whereas NF-kappaB has potent antiapoptotic function in most cell types, it was reported that in pancreatic beta cells it serves a proapoptotic function and may contribute to the pathogenesis of autoimmune type 1 diabetes. To investigate the role of beta cell NF-kappaB in autoimmune diabetes, we produced transgenic mice expressing a nondegradable form of IkappaBalpha in pancreatic beta cells (RIP-mIkappaBalpha mice). beta cells of these mice were more susceptible to killing by TNF-alpha plus IFN-gamma but more resistant to IL-1beta plus IFN-gamma than normal beta cells. Similar results were obtained with beta cells lacking IkappaB kinase beta, a protein kinase required for NF-kappaB activation. Inhibition of beta cell NF-kappaB accelerated the development of autoimmune diabetes in nonobese diabetic mice but had no effect on glucose tolerance or serum insulin in C57BL/6 mice, precluding a nonphysiological effect of transgene expression. Development of diabetes after transfer of diabetogenic CD4(+) T cells was accelerated in RIP-mIkappaBalpha/nonobese diabetic mice and was abrogated by anti-TNF therapy. These results suggest that under conditions that resemble autoimmune type 1 diabetes, the dominant effect of NF-kappaB is prevention of TNF-induced apoptosis. This differs from the proapoptotic function of NF-kappaB in IL-1beta-stimulated beta cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Induction of nuclear factor-kappaB and its downstream genes by TNF-alpha and IL-1beta has a pro-apoptotic role in pancreatic beta cells.Diabetologia. 2008 Jul;51(7):1213-25. doi: 10.1007/s00125-008-0999-7. Epub 2008 May 8. Diabetologia. 2008. PMID: 18463842
-
Nuclear factor kappaB protects pancreatic beta-cells from tumor necrosis factor-alpha-mediated apoptosis.Diabetes. 2003 May;52(5):1169-75. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.52.5.1169. Diabetes. 2003. PMID: 12716748
-
NF-kappa B hyperactivation has differential effects on the APC function of nonobese diabetic mouse macrophages.J Immunol. 2003 Feb 15;170(4):1770-80. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.170.4.1770. J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12574341
-
Role of NF-kappaB in beta-cell death.Biochem Soc Trans. 2008 Jun;36(Pt 3):334-9. doi: 10.1042/BST0360334. Biochem Soc Trans. 2008. PMID: 18481952 Review.
-
Boswellic extracts and 11-keto-ß-boswellic acids prevent type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus by suppressing the expression of proinflammatory cytokines.Phytomedicine. 2019 Oct;63:153002. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2019.153002. Epub 2019 Jun 28. Phytomedicine. 2019. PMID: 31301539 Review.
Cited by
-
Small-molecule inhibition of inflammatory β-cell death.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2013 Sep;15 Suppl 3(0 3):176-84. doi: 10.1111/dom.12158. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2013. PMID: 24003935 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Resolving the conundrum of islet transplantation by linking metabolic dysregulation, inflammation, and immune regulation.Endocr Rev. 2008 Aug;29(5):603-30. doi: 10.1210/er.2008-0006. Epub 2008 Jul 29. Endocr Rev. 2008. PMID: 18664617 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The modulatory effect of bee honey against diethyl nitrosamine and carbon tetrachloride instigated hepatocellular carcinoma in Wistar rats.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2021 Oct 14;10(6):1092-1103. doi: 10.1093/toxres/tfab094. eCollection 2021 Dec. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2021. PMID: 34992771 Free PMC article.
-
Dracaena trifasciata (Prain) Mabb leaf extract protects MIN6 pancreas-derived beta cells against the diabetic toxin streptozotocin: role of the NF-κB pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 16;16:1485952. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1485952. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40308759 Free PMC article.
-
Role of autophagy in diabetes and endoplasmic reticulum stress of pancreatic β-cells.Exp Mol Med. 2012 Feb 29;44(2):81-8. doi: 10.3858/emm.2012.44.2.030. Exp Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 22257883 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

