Identification of cellular interaction partners of the influenza virus ribonucleoprotein complex and polymerase complex using proteomic-based approaches
- PMID: 17269724
- PMCID: PMC2577182
- DOI: 10.1021/pr060432u
Identification of cellular interaction partners of the influenza virus ribonucleoprotein complex and polymerase complex using proteomic-based approaches
Abstract
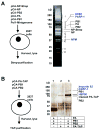
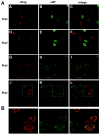
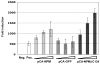
Cellular factors that associate with the influenza A viral ribonucleoprotein (vRNP) are presumed to play important roles in the viral life cycle. To date, interaction screens using individual vRNP components, such as the nucleoprotein or viral polymerase subunits, have revealed few cellular interaction partners. To improve this situation, we performed comprehensive, proteomics-based screens to identify cellular factors associated with the native vRNP and viral polymerase complexes. Reconstituted vRNPs were purified from human cells using Strep-tagged viral nucleoprotein (NP-Strep) as bait, and co-purified cellular factors were identified by mass spectrometry (MS). In parallel, reconstituted native influenza A polymerase complexes were isolated using tandem affinity purification (TAP)-tagged polymerase subunits as bait, and co-purified cellular factors were again identified by MS. Using these techniques, we identified 41 proteins that co-purified with NP-Strep-enriched vRNPs and four cellular proteins that co-purified with the viral polymerase complex. Two of the polymerase-associated factors, importin-beta3 and PARP-1, represent novel interaction partners. Most cellular proteins previously shown to interact with either viral NP and/or vRNP were also identified using our method, demonstrating its sensitivity. Co-immunoprecipitation studies in virus-infected cells using selected novel interaction partners, including nucleophosmin (NPM), confirmed their association with vRNP. Immunofluorescence analysis further revealed that NPM is recruited to sites of viral transcription and replication in infected cells. Additionally, overexpression of NPM resulted in increased viral polymerase activity, indicating its role in viral RNA synthesis. In summary, the proteomics-based approaches used in this study represent powerful tools to identify novel vRNP-associated cellular factors for further characterization.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Affinity purification of influenza virus ribonucleoprotein complexes from the chromatin of infected cells.J Vis Exp. 2012 Jun 3;(64):e4028. doi: 10.3791/4028. J Vis Exp. 2012. PMID: 22688655 Free PMC article.
-
KRT6A Restricts Influenza A Virus Replication by Inhibiting the Nuclear Import and Assembly of Viral Ribonucleoprotein Complex.Viruses. 2025 May 4;17(5):671. doi: 10.3390/v17050671. Viruses. 2025. PMID: 40431683 Free PMC article.
-
The C-Terminal Domains of the PB2 Subunit of the Influenza A Virus RNA Polymerase Directly Interact with Cellular GTPase Rab11a.J Virol. 2022 Mar 9;96(5):e0197921. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01979-21. Epub 2022 Jan 12. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 35019720 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and assembly of the influenza A virus ribonucleoprotein complex.FEBS Lett. 2013 Apr 17;587(8):1206-14. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2013.02.048. Epub 2013 Mar 13. FEBS Lett. 2013. PMID: 23499938 Review.
-
Influenza virus RNA polymerase: insights into the mechanisms of viral RNA synthesis.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2016 Aug;14(8):479-93. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro.2016.87. Epub 2016 Jul 11. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27396566 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nucleolin interacts with influenza A nucleoprotein and contributes to viral ribonucleoprotein complexes nuclear trafficking and efficient influenza viral replication.Sci Rep. 2016 Jul 4;6:29006. doi: 10.1038/srep29006. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27373907 Free PMC article.
-
Networks of Host Factors that Interact with NS1 Protein of Influenza A Virus.Front Microbiol. 2016 May 4;7:654. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00654. eCollection 2016. Front Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27199973 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear dynamics of influenza A virus ribonucleoproteins revealed by live-cell imaging studies.Virology. 2009 Nov 10;394(1):154-63. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2009.08.015. Epub 2009 Sep 9. Virology. 2009. PMID: 19744689 Free PMC article.
-
The Nucleolar Protein LYAR Facilitates Ribonucleoprotein Assembly of Influenza A Virus.J Virol. 2018 Nov 12;92(23):e01042-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01042-18. Print 2018 Dec 1. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 30209172 Free PMC article.
-
RuvB-like protein 2 is a suppressor of influenza A virus polymerases.J Virol. 2009 Jul;83(13):6429-34. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00293-09. Epub 2009 Apr 15. J Virol. 2009. PMID: 19369355 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

