Activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 5 reduces cardiac apoptosis and dysfunction via inhibition of a phosphodiesterase 3A/inducible cAMP early repressor feedback loop
- PMID: 17272811
- PMCID: PMC4115673
- DOI: 10.1161/01.RES.0000259045.49371.9c
Activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 5 reduces cardiac apoptosis and dysfunction via inhibition of a phosphodiesterase 3A/inducible cAMP early repressor feedback loop
Abstract
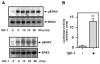
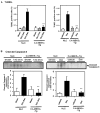
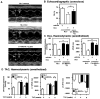
Substantial evidence suggests that the progressive loss of cardiomyocytes caused by apoptosis significantly contributes to the development of heart failure. beta-Adrenergic receptor activation and subsequent persistent phosphodiesterase 3A (PDE3A) downregulation and concomitant inducible cAMP early repressor (ICER) upregulation (PDE3A/ICER feedback loop) has been proposed to play a key role in the pathogenesis of cardiomyocyte apoptosis. In contrast, insulin-like growth factor-1 can activate cell survival pathways, providing protection against cell death and restoring muscle function. In this study, we found that insulin-like growth factor-1 activates extracellular signal-regulated kinase 5 (ERK5) and inhibits PDE3A/ICER feedback loop. Insulin-like growth factor-1 normalized isoproterenol-mediated PDE3A downregulation and ICER upregulation via ERK5/MEF2 activation, and also inhibited isoproterenol-induced myocyte apoptosis. To determine the physiological relevance of ERK5 activation in regulating PDE3A/ICER feedback loop, we investigated the PDE3A/ICER expression and cardiomyocyte apoptosis in transgenic mice with cardiac specific expression of a constitutively active form of mitogen-activated protein (MAP)/extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase (ERK) kinase 5alpha (MEK5alpha) (CA-MEK5alpha-Tg). In wild-type mice, pressure overload- or doxorubicin-induced significant reduction of PDE3A expression and subsequent ICER induction. Cardiac specific expression of CA-MEK5alpha rescued pressure overload- or doxorubicin-mediated PDE3A downregulation and ICER upregulation and inhibited myocyte apoptosis as well as subsequent cardiac dysfunction in vivo. These data suggest that preventing the feedback loop of PDE3A/ICER by ERK5 activation could inhibit progression of myocyte apoptosis as well as cardiac dysfunction. These data suggest a new therapeutic paradigm for end stage of heart failure by inhibiting the PDE3A/ICER feedback loop via activating ERK5.
Figures





Similar articles
-
A positive feedback loop of phosphodiesterase 3 (PDE3) and inducible cAMP early repressor (ICER) leads to cardiomyocyte apoptosis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Oct 11;102(41):14771-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0506489102. Epub 2005 Sep 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 16186489 Free PMC article.
-
Functional role of phosphodiesterase 3 in cardiomyocyte apoptosis: implication in heart failure.Circulation. 2005 May 17;111(19):2469-2476. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000165128.39715.87. Epub 2005 May 2. Circulation. 2005. PMID: 15867171 Free PMC article.
-
Novel role of C terminus of Hsc70-interacting protein (CHIP) ubiquitin ligase on inhibiting cardiac apoptosis and dysfunction via regulating ERK5-mediated degradation of inducible cAMP early repressor.FASEB J. 2010 Dec;24(12):4917-28. doi: 10.1096/fj.10-162636. Epub 2010 Aug 19. FASEB J. 2010. PMID: 20724525 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of phosphodiesterase 3 and inducible cAMP early repressor in the heart.Circ Res. 2007 Mar 2;100(4):489-501. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000258451.44949.d7. Circ Res. 2007. PMID: 17332439 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Platelet cyclic adenosine monophosphate phosphodiesterases: targets for regulating platelet-related thrombosis.Semin Thromb Hemost. 2004 Aug;30(4):451-60. doi: 10.1055/s-2004-833480. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2004. PMID: 15354266 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanisms of the cyclic nucleotide cross-talk signaling network in cardiac L-type calcium channel regulation.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2017 May;106:29-44. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2017.01.013. Epub 2017 Mar 29. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2017. PMID: 28365422 Free PMC article.
-
Signalosomes as Therapeutic Targets.Prog Pediatr Cardiol. 2008 Apr;25(1):51-56. doi: 10.1016/j.ppedcard.2007.11.012. Prog Pediatr Cardiol. 2008. PMID: 19343079 Free PMC article.
-
Long pentraxin PTX3 exacerbates pressure overload-induced left ventricular dysfunction.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e53133. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053133. Epub 2013 Jan 23. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23372656 Free PMC article.
-
Differential regulation of diacylglycerol kinase isoform in human failing hearts.J Cardiothorac Surg. 2011 May 8;6:65. doi: 10.1186/1749-8090-6-65. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2011. PMID: 21548979 Free PMC article.
-
G Protein-Coupled Receptor-G-Protein βγ-Subunit Signaling Mediates Renal Dysfunction and Fibrosis in Heart Failure.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017 Jan;28(1):197-208. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2015080852. Epub 2016 Jun 13. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 27297948 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kang PM, Izumo S. Apoptosis and heart failure: a critical review of the literature. Circ Res. 2000;86:1107–1113. - PubMed
-
- Olivetti G, Abbi R, Quaini F, Kajstura J, Cheng W, Nitahara JA, Quaini E, Di Loreto C, Beltrami CA, Krajewski S, Reed JC, Anversa P. Apoptosis in the failing human heart. N Engl J Med. 1997;336:1131–1141. - PubMed
-
- Lohse MJ, Engelhardt S, Eschenhagen T. What is the role of beta-adrenergic signaling in heart failure? Circ Res. 2003;93:896–906. - PubMed
-
- Wollert KC, Drexler H. Regulation of cardiac remodeling by nitric oxide: focus on cardiac myocyte hypertrophy and apoptosis. Heart Fail Rev. 2002;7:317–325. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

