The integrated stress response prevents demyelination by protecting oligodendrocytes against immune-mediated damage
- PMID: 17273557
- PMCID: PMC1783809
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI29571
The integrated stress response prevents demyelination by protecting oligodendrocytes against immune-mediated damage
Abstract
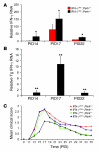
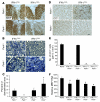
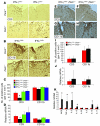
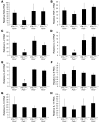
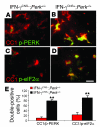
In response to ER stress, the pancreatic endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK) coordinates an adaptive program known as the integrated stress response (ISR) by phosphorylating the alpha subunit of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 (eIF2alpha). IFN-gamma, which activates the ER stress response in oligodendrocytes, is believed to play a critical role in the immune-mediated CNS disorder multiple sclerosis (MS) and its mouse model, experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). Here we report that CNS delivery of IFN-gamma before EAE onset ameliorated the disease course and prevented demyelination, axonal damage, and oligodendrocyte loss. The beneficial effects of IFN-gamma were accompanied by PERK activation in oligodendrocytes and were abrogated in PERK-deficient animals. Our results indicate that IFN-gamma activation of PERK in mature oligodendrocytes attenuates EAE severity and suggest that therapeutic approaches to activate the ISR could prove beneficial in MS.
Figures
Comment in
-
A little stress is good: IFN-gamma, demyelination, and multiple sclerosis.J Clin Invest. 2007 Feb;117(2):297-9. doi: 10.1172/JCI31254. J Clin Invest. 2007. PMID: 17273549 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Harding H.P., et al. An integrated stress response regulates amino acid metabolism and resistance to oxidative stress. Mol. Cell. 2003;11:619–633. - PubMed
-
- Proud C.G. eIF2 and the control of cell physiology. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2005;16:3–12. - PubMed
-
- Buntinx M., Stinissen P., Steels P., Ameloot M., Raus J. Immune-mediated oligodendrocyte injury in multiple sclerosis: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic interventions. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2002;22:391–424. - PubMed
-
- Frohman E.M., Racke M.K., Raine C.S. Multiple sclerosis—the plaque and its pathogenesis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006;354:942–955. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

