Efficiency and cost of economical brain functional networks
- PMID: 17274684
- PMCID: PMC1794324
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.0030017
Efficiency and cost of economical brain functional networks
Abstract
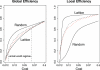
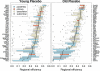
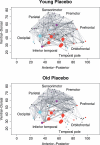
Brain anatomical networks are sparse, complex, and have economical small-world properties. We investigated the efficiency and cost of human brain functional networks measured using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) in a factorial design: two groups of healthy old (N = 11; mean age = 66.5 years) and healthy young (N = 15; mean age = 24.7 years) volunteers were each scanned twice in a no-task or "resting" state following placebo or a single dose of a dopamine receptor antagonist (sulpiride 400 mg). Functional connectivity between 90 cortical and subcortical regions was estimated by wavelet correlation analysis, in the frequency interval 0.06-0.11 Hz, and thresholded to construct undirected graphs. These brain functional networks were small-world and economical in the sense of providing high global and local efficiency of parallel information processing for low connection cost. Efficiency was reduced disproportionately to cost in older people, and the detrimental effects of age on efficiency were localised to frontal and temporal cortical and subcortical regions. Dopamine antagonism also impaired global and local efficiency of the network, but this effect was differentially localised and did not interact with the effect of age. Brain functional networks have economical small-world properties-supporting efficient parallel information transfer at relatively low cost-which are differently impaired by normal aging and pharmacological blockade of dopamine transmission.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Strogatz SH. Exploring complex networks. Nature. 2001;410:268–276. - PubMed
-
- Albert R, Barabási AL. Statistical mechanics of complex networks. Rev Mod Phys. 2002;74:47–97.
-
- Sporns O, Chialvo DR, Kaiser M, Hilgetag CC. Organization, development and function of complex brain networks. Trends Cogn Sci. 2004;8:418–425. - PubMed
-
- Salvador R, Suckling J, Coleman M, Pickard JD, Menon DK, et al. Neurophysiological architecture of functional magnetic resonance images of human brain. Cereb Cortex. 2005;15:1332–1342. - PubMed
-
- Watts DJ, Strogatz SH. Collective dynamics of “small-world” networks. Nature. 1998;393:440–442. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

