New small nuclear RNA gene-like transcriptional units as sources of regulatory transcripts
- PMID: 17274687
- PMCID: PMC1790723
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.0030001
New small nuclear RNA gene-like transcriptional units as sources of regulatory transcripts
Abstract
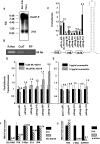
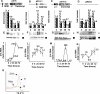
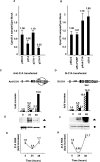
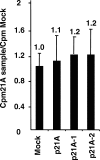
By means of a computer search for upstream promoter elements (distal sequence element and proximal sequence element) typical of small nuclear RNA genes, we have identified in the human genome a number of previously unrecognized, putative transcription units whose predicted products are novel noncoding RNAs with homology to protein-coding genes. By elucidating the function of one of them, we provide evidence for the existence of a sense/antisense-based gene-regulation network where part of the polymerase III transcriptome could control its polymerase II counterpart.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests. The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Reis EM, Nakaya HI, Louro R, Canavez FC, Flatschart AV, et al. Antisense intronic non-coding RNA levels correlate to the degree of tumor differentiation in prostate cancer. Oncogene. 2004;23:6684–6692. - PubMed
-
- Yelin R, Dahary D, Sorek R, Levanon EY, Goldstein O, et al. Widespread occurrence of antisense transcription in the human genome. Nat Biotechnol. 2003;21:379–386. - PubMed
-
- Mattick JS. RNA regulation: A new genetics? Nat Rev Genet. 2004;5:316–323. - PubMed
-
- Mattick JS, Makunin IV. Non-coding RNA [review] Hum Mol Genet. 2006;15:17–29. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

