The role of bone morphogenetic protein 4 in inner ear development and function
- PMID: 17275231
- PMCID: PMC1868473
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heares.2006.12.010
The role of bone morphogenetic protein 4 in inner ear development and function
Abstract
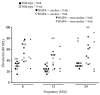
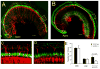
Bone Morphogenetic Protein 4 (BMP4) is a member of the TGF-beta superfamily and is known to be important for the normal development of many tissues and organs, including the inner ear. Bmp4 homozygous null mice die as embryos, but Bmp4 heterozygous null (Bmp4(+/-)) mice are viable and some adults exhibit a circling phenotype, suggestive of an inner ear defect. To understand the role of BMP4 in inner ear development and function, we have begun to study C57BL/6 Bmp4(+/-) mice. Quantitative testing of the vestibulo-collic reflex, which helps maintain head stability, demonstrated that Bmp4(+/-) mice that exhibit circling behavior have a poor response in the yaw axis, consistent with semicircular canal dysfunction. Although the hair cells of the ampullae were grossly normal, the stereocilia were greatly reduced in number. Auditory brainstem responses showed that Bmp4(+/-) mice have elevated hearing thresholds and immunohistochemical staining demonstrated decreased numbers of neuronal processes in the organ of Corti. Thus Bmp4(+/-) mice have structural and functional deficits in the inner ear.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Bone morphogenetic proteins and inner ear development.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2019 Feb.;20(2):131-145. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B1800084. Epub 2018 Aug 4. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2019. PMID: 30112880 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic modification of the inner ear lateral semicircular canal phenotype of the Bmp4 haplo-insufficient mouse.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010 Apr 9;394(3):780-5. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.03.069. Epub 2010 Mar 15. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010. PMID: 20233579
-
Bmp4 is essential for the formation of the vestibular apparatus that detects angular head movements.PLoS Genet. 2008 Apr 11;4(4):e1000050. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000050. PLoS Genet. 2008. PMID: 18404215 Free PMC article.
-
Ectopic noggin blocks sensory and nonsensory organ morphogenesis in the chicken inner ear.Dev Biol. 1999 Dec 1;216(1):369-81. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1999.9457. Dev Biol. 1999. PMID: 10588886
-
MicroRNAs in inner ear biology and pathogenesis.Hear Res. 2012 May;287(1-2):6-14. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2012.03.008. Epub 2012 Mar 29. Hear Res. 2012. PMID: 22484222 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bone morphogenetic proteins and inner ear development.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2019 Feb.;20(2):131-145. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B1800084. Epub 2018 Aug 4. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2019. PMID: 30112880 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of FoxG1 in the Inner Ear.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Dec 3;8:614954. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.614954. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 33344461 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research Progress of Hair Cell Protection Mechanism.Neural Plast. 2020 Oct 9;2020:8850447. doi: 10.1155/2020/8850447. eCollection 2020. Neural Plast. 2020. PMID: 33133179 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mutation of Rubie, a novel long non-coding RNA located upstream of Bmp4, causes vestibular malformation in mice.PLoS One. 2012;7(1):e29495. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029495. Epub 2012 Jan 12. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22253730 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Characterization of Subdomain Specification of Cochlear Duct Based on Foxg1 and Gata3.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 26;25(23):12700. doi: 10.3390/ijms252312700. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684410 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson DW, Probst FJ, Belyantseva IA, Fridell RA, Beyer L, Martin DM, Wu D, Kachar B, Friedman TB, Raphael Y, Camper SA. The motor and tail regions of myosin XV are critical for normal structure and function of auditory and vestibular hair cells. Hum Mol Genet. 2000;9:1729–38. - PubMed
-
- Barald KF, Kelley MW. From placode to polarization: new tunes in inner ear development. Development. 2004;131:4119–30. - PubMed
-
- Bermingham NA, Hassan BA, Price SD, Vollrath MA, Ben-Arie N, Eatock RA, Bellen HJ, Lysakowski A, Zoghbi HY. Math1: an essential gene for the generation of inner ear hair cells. Science. 1999;284:1837–41. - PubMed
-
- Beyer LA, Odeh H, Probst FJ, Lambert EH, Dolan DF, Camper SA, Kohrman DC, Raphael Y. Hair cells in the inner ear of the pirouette and shaker 2 mutant mice. J Neurocytol. 2000;29:227–40. - PubMed
-
- Bianchi LM, Dolnick R, Medd A, Cohan CS. Developmental changes in growth factors released by the embryonic inner ear. Exp Neurol. 1998;150:98–106. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

