Heat shock protein gp96 is a master chaperone for toll-like receptors and is important in the innate function of macrophages
- PMID: 17275357
- PMCID: PMC2847270
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2006.12.005
Heat shock protein gp96 is a master chaperone for toll-like receptors and is important in the innate function of macrophages
Abstract
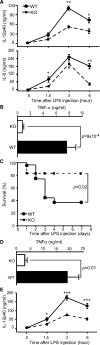
gp96 is an endoplasmic reticulum chaperone for cell-surface Toll-like receptors (TLRs). Little is known about its roles in chaperoning other TLRs or in the biology of macrophage in vivo. We generated a macrophage-specific gp96-deficient mouse. Despite normal development and activation by interferon-gamma, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and interleukin-1beta, the mutant macrophages failed to respond to ligands of both cell-surface and intracellular TLRs including TLR2, TLR4, TLR5, TLR7, and TLR9. Furthermore, we found that TLR4 and TLR9 preferentially interacted with a super-glycosylated gp96 species. The categorical loss of TLRs in gp96-deficient macrophages operationally created a conditional and cell-specific TLR null mouse. These mice were resistant to endotoxin shock but were highly susceptible to Listeria monocytogenes. Our results demonstrate that gp96 is the master chaperone for TLRs and that macrophages, but not other myeloid cells, are the dominant source of proinflammatory cytokines during endotoxemia and Listeria infections.
Figures
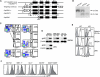
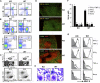
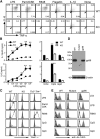
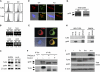

Comment in
-
gp96 leads the way for toll-like receptors.Immunity. 2007 Feb;26(2):141-3. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2007.02.003. Immunity. 2007. PMID: 17307701 Review.
References
-
- Akira S, Takeda K. Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004;4:499–511. - PubMed
-
- Argon Y, Simen BB. GRP94, an ER chaperone with protein and peptide binding properties. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 1999;10:495–505. - PubMed
-
- Barton GM, Kagan JC, Medzhitov R. Intracellular localization of Toll-like receptor 9 prevents recognition of self DNA but facilitates access to viral DNA. Nat. Immunol. 2006;7:49–56. - PubMed
-
- Bettelli E, Carrier Y, Gao W, Korn T, Strom TB, Oukka M, Weiner HL, Kuchroo VK. Reciprocal developmental pathways for the generation of pathogenic effector TH17 and regulatory T cells. Nature. 2006;441:235–238. - PubMed
-
- Beutler B, Milsark IW, Cerami AC. Passive immunization against cachectin/tumor necrosis factor protects mice from lethal effect of endotoxin. Science. 1985;229:869–871. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

