Primary pigmented nodular adrenocortical disease reveals insulin-like growth factor binding protein-2 regulation by protein kinase A
- PMID: 17280861
- PMCID: PMC2577759
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ghir.2006.12.004
Primary pigmented nodular adrenocortical disease reveals insulin-like growth factor binding protein-2 regulation by protein kinase A
Abstract
Objective: Primary pigmented nodular adrenocortical disease (PPNAD) can occur as an isolated trait or part of Carney complex, a familial lentiginosis-multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome frequently caused by mutations in PRKAR1A, which encodes the 1alpha regulatory subunit of protein kinase A (PKA). Because alterations in the insulin-like growth factor (IGF) axis, particularly IGF-II and IGF binding protein (IGFBP)-2 overexpression, have been implicated in sporadic adrenocortical tumors, we sought to examine the IGF axis in PPNAD.
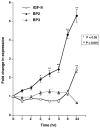
Design: RNA samples and paraffin-embedded sections were procured from adrenalectomy specimens of patients with PPNAD. Changes in expression of IGF axis components were evaluated by real-time quantitative RT-PCR and immunohistochemistry. NCI-H295R cells were used to study PKA and IGF axis signaling in adrenocortical cells in vitro.
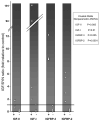
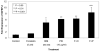
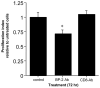
Results: IGFBP-2 mRNA level distinguished between the two genetic subtypes of this disease; increased IGFBP-2 expression in PRKAR1A mutation-positive PPNAD tissues was also confirmed by immunohistochemistry. Moreover, PKA inhibitors increased IGFBP-2 expression in NCI-H295R adrenocortical cells, and anti-IGFBP-2 antibody reduced their proliferation.
Conclusions: IGFBP-2 expression is increased in PPNAD caused by PRKAR1A mutations, and in adrenocortical cancer cells. This is the first evidence for PKA-dependent regulation of IGFBP-2 expression in adrenocortical cells.
Figures

References
-
- Shenoy BV, Carpenter PC, Carney JA. Bilateral primary pigmented nodular adrenocortical disease. Rare cause of the Cushing syndrome. Am J Surg Pathol. 1984;8:335–344. - PubMed
-
- Lacroix A, Bourdeau I. Bilateral adrenal Cushing's syndrome: macronodular adrenal hyperplasia and primary pigmented nodular adrenocortical disease. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2005;34:441–58. x. - PubMed
-
- Stratakis CA, Kirschner LS, Carney JA. Clinical and molecular features of the Carney complex: diagnostic criteria and recommendations for patient evaluation. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001;86:4041–4046. - PubMed
-
- Kirschner LS, Carney JA, Pack SD, et al. Mutations of the gene encoding the protein kinase A type I-alpha regulatory subunit in patients with the Carney complex. Nat Genet. 2000;26:89–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

