c-Jun homodimers can function as a context-specific coactivator
- PMID: 17283046
- PMCID: PMC1899927
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00936-06
c-Jun homodimers can function as a context-specific coactivator
Abstract
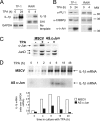
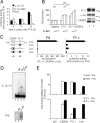
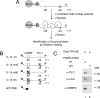
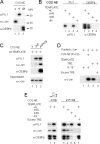
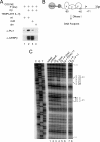
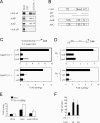
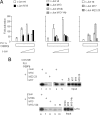
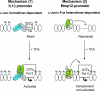
Transcription factors can function as DNA-binding-specific activators or as coactivators. c-Jun drives gene expression via binding to AP-1 sequences or as a cofactor for PU.1 in macrophages. c-Jun heterodimers bind AP-1 sequences with higher affinity than homodimers, but how c-Jun works as a coactivator is unknown. Here, we provide in vitro and in vivo evidence that c-Jun homodimers are recruited to the interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta) promoter in the absence of direct DNA binding via protein-protein interactions with DNA-anchored PU.1 and CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta (C/EBPbeta). Unexpectedly, the interaction interface with PU.1 and C/EBPbeta involves four of the residues within the basic domain of c-Jun that contact DNA, indicating that the capacities of c-Jun to function as a coactivator or as a DNA-bound transcription factor are mutually exclusive. Our observations indicate that the IL-1beta locus is occupied by PU.1 and C/EBPbeta and poised for expression and that c-Jun enhances transcription by facilitating a rate-limiting step, the assembly of the RNA polymerase II preinitiation complex, with minimal effect on the local chromatin status. We propose that the basic domain of other transcription factors may also be redirected from a DNA interaction mode to a protein-protein interaction mode and that this switch represents a novel mechanism regulating gene expression profiles.
Figures


Similar articles
-
c-Jun is a JNK-independent coactivator of the PU.1 transcription factor.J Biol Chem. 1999 Feb 19;274(8):4939-46. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.8.4939. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 9988737
-
A combined computational and experimental approach reveals the structure of a C/EBPβ-Spi1 interaction required for IL1B gene transcription.J Biol Chem. 2018 Dec 28;293(52):19942-19956. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.005627. Epub 2018 Oct 24. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 30355733 Free PMC article.
-
The macrosialin promoter directs high levels of transcriptional activity in macrophages dependent on combinatorial interactions between PU.1 and c-Jun.J Biol Chem. 1998 Feb 27;273(9):5389-99. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.9.5389. J Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9479000
-
C/EBP alpha:AP-1 leucine zipper heterodimers bind novel DNA elements, activate the PU.1 promoter and direct monocyte lineage commitment more potently than C/EBP alpha homodimers or AP-1.Oncogene. 2008 Apr 24;27(19):2772-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1210940. Epub 2007 Nov 19. Oncogene. 2008. PMID: 18026136 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of the role of activator protein-1 on transcription of the mouse steroidogenic acute regulatory protein gene.Mol Endocrinol. 2004 Mar;18(3):558-73. doi: 10.1210/me.2003-0223. Epub 2003 Dec 12. Mol Endocrinol. 2004. PMID: 14673133
Cited by
-
Pleiotropic action of AP-1 in v-Src-transformed cells.J Virol. 2011 Jul;85(13):6725-35. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01013-10. Epub 2011 Apr 20. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21507983 Free PMC article.
-
The LMO2 oncogene regulates DNA replication in hematopoietic cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Feb 2;113(5):1393-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1515071113. Epub 2016 Jan 13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 26764384 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of the Transcription Factors Sp1/Sp3 and AP-1 to Clusterin Gene Expression during Corneal Wound Healing of Tissue-Engineered Human Corneas.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 17;22(22):12426. doi: 10.3390/ijms222212426. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34830308 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Activator Protein-1 (AP-1) Family Members in CD30-Positive Lymphomas.Cancers (Basel). 2018 Mar 28;10(4):93. doi: 10.3390/cancers10040093. Cancers (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29597249 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of a minimal cis-element and cognate trans-factor(s) required for induction of Rac2 gene expression during K562 cell differentiation.Gene. 2009 Jul 1;440(1-2):63-72. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2009.04.005. Epub 2009 Apr 17. Gene. 2009. PMID: 19376210 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agalioti, T., G. Chen, and D. Thanos. 2002. Deciphering the transcriptional histone acetylation code for a human gene. Cell 111:381-392. - PubMed
-
- Agalioti, T., S. Lomvardas, B. Parekh, J. Yie, T. Maniatis, and D. Thanos. 2000. Ordered recruitment of chromatin modifying and general transcription factors to the IFN-beta promoter. Cell 103:667-678. - PubMed
-
- Allegretto, E. A., T. Smeal, P. Angel, B. M. Spiegelman, and M. Karin. 1990. DNA-binding activity of Jun is increased through its interaction with Fos. J. Cell Biochem. 42:193-206. - PubMed
-
- Angel, P., M. Imagawa, R. Chiu, B. Stein, R. J. Imbra, H. J. Rahmsdorf, C. Jonat, P. Herrlich, and M. Karin. 1987. Phorbol ester-inducible genes contain a common cis element recognized by a TPA-modulated trans-acting factor. Cell 49:729-739. - PubMed
-
- Bassuk, A. G., and J. M. Leiden. 1995. A direct physical association between ETS and AP-1 transcription factors in normal human T cells. Immunity 3:223-237. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
