Role for furin in tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced activation of the matrix metalloproteinase/sphingolipid mitogenic pathway
- PMID: 17283058
- PMCID: PMC1899924
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01485-06
Role for furin in tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced activation of the matrix metalloproteinase/sphingolipid mitogenic pathway
Abstract
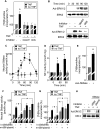
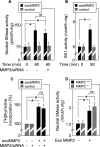
Neutral sphingomyelinase (nSMase), the initial enzyme of the sphingolipid signaling pathway, is thought to play a key role in cellular responses to tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha), such as inflammation, proliferation, and apoptosis. The mechanism of TNF-alpha-induced nSMase activation is only partly understood. Using biochemical, molecular, and pharmacological approaches, we found that nSMase activation triggered by TNF-alpha is required for TNF-alpha-induced proliferation and in turn requires a proteolytic cascade involving furin, membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP), and MMP2, and leading finally to extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) phosphorylation and DNA synthesis, in smooth muscle cells (SMC) and fibroblasts. Pharmacological and molecular inhibitors of MMPs (batimastat), furin (alpha1-PDX inhibitor-transfected SMC), MT1-MMP (SMC overexpressing a catalytically inactive MT1-MMP), MMP2 (fibroblasts from MMP2(-/-) mice), and small interfering RNA (siRNA) strategies (siRNAs targeting furin, MT1-MMP, MMP2, and nSMase) resulted in near-complete inhibition of the activation of nSMase, sphingosine kinase-1, and ERK1/2 and of subsequent DNA synthesis. Exogenous MT1-MMP activated nSMase and SMC proliferation in normal but not in MMP2(-/-) fibroblasts, whereas exogenous MMP2 was active on both normal and MMP2(-/-) fibroblasts. Altogether these findings highlight a pivotal role for furin, MT1-MMP, and MMP2 in TNF-alpha-induced sphingolipid signaling, and they identify this system as a possible target to inhibit SMC proliferation in vascular diseases.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Role for matrix metalloproteinase-2 in oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced activation of the sphingomyelin/ceramide pathway and smooth muscle cell proliferation.Circulation. 2004 Aug 3;110(5):571-8. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000136995.83451.1D. Epub 2004 Jul 26. Circulation. 2004. PMID: 15277330
-
MAO-A-induced mitogenic signaling is mediated by reactive oxygen species, MMP-2, and the sphingolipid pathway.Free Radic Biol Med. 2007 Jul 1;43(1):80-9. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2007.03.036. Epub 2007 Apr 10. Free Radic Biol Med. 2007. PMID: 17561096
-
Integrin alpha(v)beta(3), metalloproteinases, and sphingomyelinase-2 mediate urokinase mitogenic effect.Cell Signal. 2009 Dec;21(12):1925-34. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2009.08.010. Epub 2009 Sep 6. Cell Signal. 2009. PMID: 19735728
-
Ceramide/sphingosine/sphingosine 1-phosphate metabolism on the cell surface and in the extracellular space.Cell Signal. 2007 Feb;19(2):229-37. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2006.07.001. Epub 2006 Sep 11. Cell Signal. 2007. PMID: 16963225 Review.
-
[Sphingolipid-mediated apoptotic signaling pathways].J Soc Biol. 2003;197(3):217-21. J Soc Biol. 2003. PMID: 14708343 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Functional Roles of Furin in Cardio-Cerebrovascular Diseases.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2024 Feb 7;7(3):570-585. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.3c00325. eCollection 2024 Mar 8. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2024. PMID: 38481703 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Influence of a Coronary Artery Disease-Associated Genetic Variant on FURIN Expression and Effect of Furin on Macrophage Behavior.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018 Aug;38(8):1837-1844. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.118.311030. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018. PMID: 29976768 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis B virus X protein is capable of down-regulating protein level of host antiviral protein APOBEC3G.Sci Rep. 2017 Jan 18;7:40783. doi: 10.1038/srep40783. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28098260 Free PMC article.
-
Neutral sphingomyelinase 2 (nSMase2) is the primary neutral sphingomyelinase isoform activated by tumour necrosis factor-α in MCF-7 cells.Biochem J. 2011 Apr 15;435(2):381-90. doi: 10.1042/BJ20101752. Biochem J. 2011. PMID: 21303347 Free PMC article.
-
Reoxygenation of hypoxic glioblastoma multiforme cells potentiates the killing effect of an interleukin-13-based cytotoxin.Clin Cancer Res. 2009 Jan 1;15(1):160-8. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-2151. Clin Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19118043 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adam, D., K. Wiegmann, S. Adam-Klages, A. Ruff, and M. Kronke. 1996. A novel cytoplasmic domain of the p55 tumor necrosis factor receptor initiates the neutral sphingomyelinase pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 271:14617-14622. - PubMed
-
- Aggarwal, B. 2003. Signalling pathways of the TNF superfamily: a double-edged sword. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 3:745-756. - PubMed
-
- Aubin, I., C. P. Adams, S. Opsahl, D. Septier, C. E. Bishop, N. Auge, R. Salvayre, A. Negre-Salvayre, M. Goldberg, J. L. Guenet, and C. Poirier. 2005. A deletion in the gene encoding sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase 3 (Smpd3) results in osteogenesis and dentinogenesis imperfecta in the mouse. Nat. Genet. 37:803-805. - PubMed
-
- Auge, N., N. Andrieu, A. Negre-Salvayre, J. C. Thiers, T. Levade, and R. Salvayre. 1996. The sphingomyelin-ceramide signaling pathway is involved in oxidized low density lipoprotein-induced cell proliferation. J. Biol. Chem. 271:19251-19255. - PubMed
-
- Auge, N., F. Maupas-Schwalm, M. Elbaz, J. C. Thiers, A. Waysbort, S. Itohara, H. W. Krell, R. Salvayre, and A. Negre-Salvayre. 2004. Role for matrix metalloproteinase-2 in oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced activation of the sphingomyelin/ceramide pathway and smooth muscle cell proliferation. Circulation 110:571-578. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
