Resistance to Pseudomonas aeruginosa chronic lung infection requires cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator-modulated interleukin-1 (IL-1) release and signaling through the IL-1 receptor
- PMID: 17283089
- PMCID: PMC1865697
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.01980-06
Resistance to Pseudomonas aeruginosa chronic lung infection requires cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator-modulated interleukin-1 (IL-1) release and signaling through the IL-1 receptor
Abstract
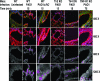
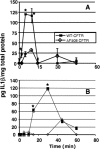
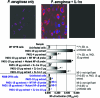
Innate immunity is critical for clearing Pseudomonas aeruginosa from the lungs. In response to P. aeruginosa infection, a central transcriptional regulator of innate immunity-NF-kappaB-is translocated within 15 min to the nuclei of respiratory epithelial cells expressing wild-type (WT) cystic fibrosis (CF) transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR). P. aeruginosa clearance from lungs is impaired in CF, and rapid NF-kappaB nuclear translocation is defective in cells with mutant or missing CFTR. We used WT and mutant P. aeruginosa and strains of transgenic mice lacking molecules involved in innate immunity to identify additional mediators required for P. aeruginosa-induced rapid NF-kappaB nuclear translocation in lung epithelia. We found neither Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) nor TLR4 nor TLR5 were required for this response. However, both MyD88-deficient mice and interleukin-1 receptor (IL-1R)-deficient mice failed to rapidly translocate NF-kappaB to the nuclei of respiratory epithelial cells in response to P. aeruginosa. Cultured human bronchial epithelial cells rapidly released IL-1beta in response to P. aeruginosa; this process was maximized by expression of WT-CFTR and dramatically muted in cells with DeltaF508-CFTR. The IL-1R antagonist blocked P. aeruginosa-induced NF-kappaB nuclear translocation. Oral inoculation via drinking water of IL-1R knockout mice resulted in higher rates of lung colonization and elevated P. aeruginosa-specific antibody titers in a manner analogous to that of CFTR-deficient mice. Overall, rapid IL-1 release and signaling through IL-1R represent key steps in the innate immune response to P. aeruginosa infection, and this process is deficient in cells lacking functional CFTR.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Influence of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator on gene expression in response to Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection of human bronchial epithelial cells.Infect Immun. 2005 Oct;73(10):6822-30. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.10.6822-6830.2005. Infect Immun. 2005. PMID: 16177360 Free PMC article.
-
Pseudomonas aeruginosa-induced apoptosis is defective in respiratory epithelial cells expressing mutant cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2003 Aug;29(2):188-97. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.4898. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2003. PMID: 12878584
-
Localization of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator to lipid rafts of epithelial cells is required for Pseudomonas aeruginosa-induced cellular activation.J Immunol. 2004 Jan 1;172(1):418-25. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.172.1.418. J Immunol. 2004. PMID: 14688350
-
Role of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator in innate immunity to Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Aug 1;97(16):8822-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.16.8822. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. PMID: 10922041 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phagocytic and signaling innate immune receptors: are they dysregulated in cystic fibrosis in the fight against Pseudomonas aeruginosa?Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014 Jul;52:103-7. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2014.01.013. Epub 2014 Feb 5. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24508137 Review.
Cited by
-
CFTR is a negative regulator of NFkappaB mediated innate immune response.PLoS One. 2009;4(2):e4664. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0004664. Epub 2009 Feb 27. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19247502 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and function of the Type III secretion system of Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2012 Dec;13(8):831-42. doi: 10.2174/138920312804871210. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2012. PMID: 23305368 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inescapable need for neutrophils as mediators of cellular innate immunity to acute Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia.Infect Immun. 2009 Dec;77(12):5300-10. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00501-09. Epub 2009 Oct 5. Infect Immun. 2009. PMID: 19805527 Free PMC article.
-
The Pseudomonas aeruginosa protease LasB directly activates IL-1β.EBioMedicine. 2020 Oct;60:102984. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102984. Epub 2020 Sep 23. EBioMedicine. 2020. PMID: 32979835 Free PMC article.
-
Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator and caveolin-1 regulate epithelial cell internalization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2009 Aug;297(2):C263-77. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00527.2008. Epub 2009 Apr 22. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19386787 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adamo, R., S. Sokol, G. Soong, M. I. Gomez, and A. Prince. 2004. Pseudomonas aeruginosa flagella activate airway epithelial cells through asialoGM1 and Toll-like receptor 2 as well as Toll-like receptor 5. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 30:627-634. - PubMed
-
- Amura, C. R., P. A. Fontan, N. Sanjuan, and D. O. Sordelli. 1994. The effect of treatment with interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor on Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung infection in a granulocytopenic mouse model. Clin. Immunol. Immunopathol. 73:261-266. - PubMed
-
- Banwart, B., M. L. Splaingard, P. M. Farrell, M. J. Rock, P. L. Havens, J. Moss, M. E. Ehrmantraut, D. W. Frank, and J. T. Barbieri. 2002. Children with cystic fibrosis produce an immune response against exoenzyme S, a type III cytotoxin of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Infect. Dis. 185:269-270. - PubMed
-
- Blander, J. M., and R. Medzhitov. 2006. Toll-dependent selection of microbial antigens for presentation by dendritic cells. Nature 440:808-812. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

