Coinfection with Schistosoma mansoni reactivates viremia in rhesus macaques with chronic simian-human immunodeficiency virus clade C infection
- PMID: 17283092
- PMCID: PMC1865689
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.01703-06
Coinfection with Schistosoma mansoni reactivates viremia in rhesus macaques with chronic simian-human immunodeficiency virus clade C infection
Abstract
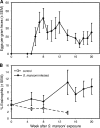
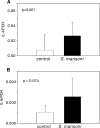
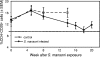
We tested the hypothesis that helminth parasite coinfection would intensify viremia and accelerate disease progression in monkeys chronically infected with an R5 simian-human immunodeficiency virus (SHIV) encoding a human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) clade C envelope. Fifteen rhesus monkeys with stable SHIV-1157ip infection were enrolled into a prospective, randomized trial. These seropositive animals had undetectable viral RNA and no signs of immunodeficiency. Seven animals served as virus-only controls; eight animals were exposed to Schistosoma mansoni cercariae. From week 5 after parasite exposure onward, coinfected animals shed eggs in their feces, developed eosinophilia, and had significantly higher mRNA expression of the T-helper type 2 cytokine interleukin-4 (P = 0.001) than animals without schistosomiasis. Compared to virus-only controls, viral replication was significantly increased in coinfected monkeys (P = 0.012), and the percentage of their CD4(+) CD29(+) memory cells decreased over time (P = 0.05). Thus, S. mansoni coinfection significantly increased viral replication and induced T-cell subset alterations in monkeys with chronic SHIV clade C infection.
Figures

References
-
- Ahmed-Ansari, A., J. D. Powell, P. E. Jensen, T. Yehuda-Cohen, H. M. McClure, D. Anderson, P. N. Fultz, and K. W. Sell. 1990. Requirements for simian immunodeficiency virus antigen-specific in vitro proliferation of T cells from infected rhesus macaques and sooty mangabeys. AIDS 4:399-407. - PubMed
-
- Ayash-Rashkovsky, M., Z. Bentwich, and G. Borkow. 2005. TLR9 expression is related to immune activation but is impaired in individuals with chronic immune activation. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 37:2380-2394. - PubMed
-
- Baba, T. W., Y. S. Jeong, D. Pennick, R. Bronson, M. F. Greene, and R. M. Ruprecht. 1995. Pathogenicity of live, attenuated SIV after mucosal infection of neonatal macaques. Science 267:1820-1825. - PubMed
-
- Baba, T. W., V. Liska, A. H. Khimani, N. B. Ray, P. J. Dailey, D. Penninck, R. Bronson, M. F. Greene, H. M. McClure, L. N. Martin, and R. M. Ruprecht. 1999. Live attenuated, multiply deleted simian immunodeficiency virus causes AIDS in infant and adult macaques. Nat. Med. 5:194-203. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

