Regulation of exoprotein gene expression by the Staphylococcus aureus cvfB gene
- PMID: 17283102
- PMCID: PMC1865683
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.01552-06
Regulation of exoprotein gene expression by the Staphylococcus aureus cvfB gene
Abstract
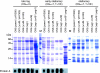
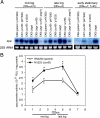
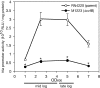
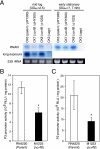
We previously reported that the cvfB gene (SA1223) of Staphylococcus aureus is responsible for the virulence of this pathogenic bacterium. We show here that the cvfB gene regulates exoprotein gene expression. In a cvfB gene deletion mutant, hemolysin, DNase, and protease production were decreased, whereas protein A expression was increased. The amount of RNAIII, the transcript from the P3 promoter in the agr locus that regulates the expression of various virulence factors, was also reduced in the cvfB mutant. In addition, P2 and P3 promoter activity in the agr locus was decreased in the mutant. Under the genetic background of the agr-null mutation, cvfB gene disruption decreased the production levels of DNase and protease. Moreover, the cvfB and agr double mutant was less virulent than the agr mutant in silkworms. These results suggest that the cvfB gene product contributes to the expression of virulence factors and to pathogenicity via both agr-dependent and agr-independent pathways.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Coordinated and differential control of aureolysin (aur) and serine protease (sspA) transcription in Staphylococcus aureus by sarA, rot and agr (RNAIII).Int J Med Microbiol. 2006 Oct;296(6):365-80. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2006.02.019. Epub 2006 Jun 19. Int J Med Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16782403
-
Novel DNA binding protein SarZ contributes to virulence in Staphylococcus aureus.Mol Microbiol. 2006 Dec;62(6):1601-17. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05480.x. Mol Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 17087772
-
The cvfC operon of Staphylococcus aureus contributes to virulence via expression of the thyA gene.Microb Pathog. 2010 Jul-Aug;49(1-2):1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2010.03.010. Epub 2010 Mar 27. Microb Pathog. 2010. PMID: 20347953
-
Regulation of virulence determinants in Staphylococcus aureus.Int J Med Microbiol. 2001 May;291(2):159-70. doi: 10.1078/1438-4221-00112. Int J Med Microbiol. 2001. PMID: 11437338 Review.
-
Quorum sensing-mediated regulation of staphylococcal virulence and antibiotic resistance.Future Microbiol. 2014;9(5):669-81. doi: 10.2217/fmb.14.31. Future Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24957093 Review.
Cited by
-
Animal infection models using non-mammals.Microbiol Immunol. 2020 Sep;64(9):585-592. doi: 10.1111/1348-0421.12834. Epub 2020 Aug 22. Microbiol Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32757288 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aliarcobacter butzleri from Water Poultry: Insights into Antimicrobial Resistance, Virulence and Heavy Metal Resistance.Genes (Basel). 2020 Sep 21;11(9):1104. doi: 10.3390/genes11091104. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32967159 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-Surface Phenol Soluble Modulins Regulate Staphylococcus aureus Colony Spreading.PLoS One. 2016 Oct 10;11(10):e0164523. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0164523. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27723838 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-genome sequencing of Staphylococcus aureus strain RN4220, a key laboratory strain used in virulence research, identifies mutations that affect not only virulence factors but also the fitness of the strain.J Bacteriol. 2011 May;193(9):2332-5. doi: 10.1128/JB.00027-11. Epub 2011 Mar 4. J Bacteriol. 2011. PMID: 21378186 Free PMC article.
-
CvfA protein and polynucleotide phosphorylase act in an opposing manner to regulate Staphylococcus aureus virulence.J Biol Chem. 2014 Mar 21;289(12):8420-31. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.554329. Epub 2014 Feb 3. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24492613 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cheung, A. L., A. S. Bayer, G. Zhang, H. Gresham, and Y. Q. Xiong. 2004. Regulation of virulence determinants in vitro and in vivo in Staphylococcus aureus. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 40:1-9. - PubMed
-
- Chien, Y., A. C. Manna, and A. L. Cheung. 1998. SarA level is a determinant of agr activation in Staphylococcus aureus. Mol. Microbiol. 30:991-1001. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

