Induction of monocyte chemotactic protein 1 in colonic epithelial cells by Entamoeba histolytica is mediated via the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/p65 pathway
- PMID: 17283105
- PMCID: PMC1865671
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.01442-06
Induction of monocyte chemotactic protein 1 in colonic epithelial cells by Entamoeba histolytica is mediated via the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/p65 pathway
Abstract
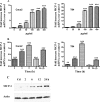
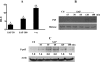
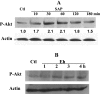
The role intestinal epithelial cells play in the pathogenesis of amebic colitis is poorly understood. Herein, we demonstrate that secreted and soluble ameba (Entamoeba histolytica) proteins (SAP) induce expression of the chemoattractant monocyte chemotactic protein (MCP) in the colonic epithelial cell lines Caco-2, T84, and LS174T. MCP-1 mRNA induction was both dose and time dependent, with peak induction occurring at 8 h and with 100 mug/ml of SAP. Significant increase in MCP-1 protein expression was observed after 12 h. SAP failed to activate any of the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways or IkappaB kinase activity. Moreover, inhibiting the classical pathway of NF-kappaB activation did not affect SAP-induced MCP-1 expression. Instead, we find that SAP-induced MCP-1 expression is dependent on posttranslational modification of the NFkappaB p65 subunit. SAP induced phosphorylation of p65 and enhanced NF-kappaB transcriptional activity, which are phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3 kinase) dependent. Treatment with PI3 kinase inhibitor LY290004 significantly abrogated the activation of Akt, p65, and MCP-1 mRNA induction. We conclude that colonic epithelial cells play a role in the initiation of inflammation by secreting chemokines in response to soluble ameba components.
Figures
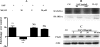

Similar articles
-
Suppression of NF-kappaB activation by Entamoeba histolytica in intestinal epithelial cells is mediated by heat shock protein 27.J Biol Chem. 2006 Sep 8;281(36):26112-20. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M601988200. Epub 2006 Jul 13. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16840786
-
Leptospiral membrane proteins stimulate pro-inflammatory chemokines secretion by renal tubule epithelial cells through toll-like receptor 2 and p38 mitogen activated protein kinase.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2006 Apr;21(4):898-910. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfi316. Epub 2005 Dec 8. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2006. PMID: 16339163
-
Degradation of the transcription factors NF-κB, STAT3, and STAT5 is involved in Entamoeba histolytica-induced cell death in Caco-2 colonic epithelial cells.Korean J Parasitol. 2014 Oct;52(5):459-69. doi: 10.3347/kjp.2014.52.5.459. Epub 2014 Oct 22. Korean J Parasitol. 2014. PMID: 25352693 Free PMC article.
-
Sesquiterpene lactones inhibit Yersinia invasin protein-induced IL-8 and MCP-1 production in epithelial cells.Int J Med Microbiol. 2005 Dec;295(8):531-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2005.07.012. Epub 2005 Sep 13. Int J Med Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 16325549
-
[Influence of atorvastatin on the expression of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in peritoneal mesothelial cells by high glucose].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2007 Oct 16;87(38):2677-80. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2007. PMID: 18167242 Chinese.
Cited by
-
The NF-kappaB p50 subunit is protective during intestinal Entamoeba histolytica infection of 129 and C57BL/6 mice.Infect Immun. 2010 Apr;78(4):1475-81. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00669-09. Epub 2010 Jan 19. Infect Immun. 2010. PMID: 20086086 Free PMC article.
-
The NF-κB Pathway: Modulation by Entamoeba histolytica and Other Protozoan Parasites.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Sep 14;11:748404. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.748404. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34595137 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prostaglandin E2 produced by Entamoeba histolytica binds to EP4 receptors and stimulates interleukin-8 production in human colonic cells.Infect Immun. 2008 Nov;76(11):5158-63. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00645-08. Epub 2008 Aug 18. Infect Immun. 2008. PMID: 18710858 Free PMC article.
-
Entamoeba histolytica: Host parasite interactions at the colonic epithelium.Tissue Barriers. 2017 Jan 2;5(1):e1283386. doi: 10.1080/21688370.2017.1283386. Tissue Barriers. 2017. PMID: 28452682 Free PMC article.
-
Cell Type-Specific Roles of NF-κB Linking Inflammation and Thrombosis.Front Immunol. 2019 Feb 4;10:85. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00085. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30778349 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bas, A., G. Forsberg, S. Hammarström, and M.-L. Hammarström. 2004. Utility of the housekeeping genes 18srRNA, β-actin and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate-dehydrogenase for normalization in real-time quantitative reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction analysis of gene expression in human T lymphocytes. Scand. J. Immunol. 59:566-573. - PubMed
-
- Bohuslav, J., L.-F. Chen, H. Kwon, Y. Mu, and W. C. Greene. 2004. p53 induces NF-κB activation by an IκB kinase-independent mechanism involving phosphorylation of p65 by ribosomal S6 kinase 1. J. Biol. Chem. 279:26115-26125. - PubMed
-
- Chen, L.-F., and W. C. Greene. 2004. Shaping the nuclear action of NF-κB. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 5:392-401. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

