Inflammatory lipoproteins purified from a toxigenic and arthritogenic strain of Mycoplasma arthritidis are dependent on Toll-like receptor 2 and CD14
- PMID: 17283106
- PMCID: PMC1865712
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00516-06
Inflammatory lipoproteins purified from a toxigenic and arthritogenic strain of Mycoplasma arthritidis are dependent on Toll-like receptor 2 and CD14
Abstract
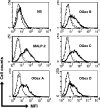
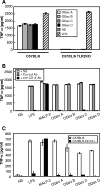
Mycoplasma arthritidis is a naturally occurring murine pathogen, and the disease model has been used extensively to understand inflammatory mechanisms. Recently, Triton X-114 extracts of a virulent strain of M. arthritidis were found to be more potent in activating macrophages than were those from an avirulent strain, suggesting a role in disease. Here, octyl glucoside extraction of cells was used to identify four distinct bioactive moieties, with molecular masses of approximately 41, 37, 34, and 17 kDa. Their bioactivities were resistant to proteinase K but were destroyed by alkaline hydrolysis and oxidation. As for MALP-2, all were dependent upon Toll-like receptor 2, but unlike MALP-2, they were also dependent upon CD14. The M. arthritidis lipoproteins exhibited infrared absorbances at 2,900 cm(-1) and 1,662 cm(-1), similar to those seen in Pam(3)-Cys-Ser-(Lys)(4). Edman degradation failed to reveal N-terminal sequences, suggesting that they were blocked and therefore might be triacylated. However, mass spectrometry of fragments revealed that the 41-kDa moiety, which binds to serum apolipoprotein A-1, had similarity with the recently described MlpD lipoprotein of M. arthritidis.
Figures



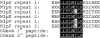

Similar articles
-
Isolation and partial purification of macrophage- and dendritic cell-activating components from Mycoplasma arthritidis: association with organism virulence and involvement with Toll-like receptor 2.Infect Immun. 2005 Sep;73(9):6039-47. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.9.6039-6047.2005. Infect Immun. 2005. PMID: 16113324 Free PMC article.
-
A microbial TLR2 agonist imparts macrophage-activating ability to apolipoprotein A-1.J Immunol. 2006 Oct 1;177(7):4826-32. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.177.7.4826. J Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16982924
-
TLR2 and TLR4 differentially regulate B7-1 resulting in distinct cytokine responses to the mycoplasma superantigen MAM as well as to disease induced by Mycoplasma arthritidis.Cell Microbiol. 2006 Mar;8(3):414-26. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2005.00630.x. Cell Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16469054
-
A potential pathogenic factor from Mycoplasma hominis is a TLR2-dependent, macrophage-activating, P50-related adhesin.Am J Reprod Immunol. 2014 Sep;72(3):285-95. doi: 10.1111/aji.12279. Epub 2014 Jun 17. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24938999
-
Mycoplasma fermentans lipoprotein M161Ag-induced cell activation is mediated by Toll-like receptor 2: role of N-terminal hydrophobic portion in its multiple functions.J Immunol. 2001 Feb 15;166(4):2610-6. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.166.4.2610. J Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11160323
Cited by
-
The Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) ligand FSL-1 is internalized via the clathrin-dependent endocytic pathway triggered by CD14 and CD36 but not by TLR2.Immunology. 2010 Jun;130(2):262-72. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2009.03232.x. Epub 2010 Jan 27. Immunology. 2010. PMID: 20113368 Free PMC article.
-
Serum lipoproteins attenuate macrophage activation and Toll-Like Receptor stimulation by bacterial lipoproteins.BMC Immunol. 2010 Sep 16;11:46. doi: 10.1186/1471-2172-11-46. BMC Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20846396 Free PMC article.
-
Mycoplasma lipoproteins and Toll-like receptors.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2009 Jan;10(1):67-76. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B0820256. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2009. PMID: 19198025 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Innate immune responses to bacterial ligands in the peripheral human lung--role of alveolar epithelial TLR expression and signalling.PLoS One. 2011;6(7):e21827. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0021827. Epub 2011 Jul 15. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21789185 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Braun, V., and K. Rehn. 1969. Chemical characterization, spatial distribution and function of a lipoprotein (murein-lipoprotein) of the E. coli cell wall. The specific effect of trypsin on the membrane structure. Eur. J. Biochem. 10:426-438. - PubMed
-
- Cole, B., A. Sawitzke, and H.-H. Mu. 2000. Mycoplasma arthritidis and its superantigen M. arthritidis mitogen as a model for inflammatory and autoimmune disease, p. 93-107. In M. W. Cunningham and R. S. Fujinami (ed.), Effects of microbes on the immune system. Lippincott, Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia, PA.
-
- Cole, B. C., and M. M. Griffiths. 1993. Triggering and exacerbation of autoimmune arthritis by the Mycoplasma arthritidis superantigen MAM. Arthritis Rheum. 36:994-1002. - PubMed
-
- Cole, B. C., H.-H. Mu, N. D. Pennock, A. Hasebe, F. V. Chan, L. R. Washburn, and M. R. Peltier. 2005. Isolation and partial purification of macrophage- and dendritic cell-activating components from Mycoplasma arthritidis: association with organism virulence and involvement with Toll-like receptor 2. Infect. Immun. 73:6039-6047. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cole, B. C., H.-H. Mu, and A. D. Sawitzke. 2000. The mycoplasma superantigen MAM: role in arthritis and immune-mediated disease. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 290:489-490. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

