X-ray fluorescence microscopy reveals large-scale relocalization and extracellular translocation of cellular copper during angiogenesis
- PMID: 17283338
- PMCID: PMC1892952
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0607238104
X-ray fluorescence microscopy reveals large-scale relocalization and extracellular translocation of cellular copper during angiogenesis
Abstract
Although copper has been reported to influence numerous proteins known to be important for angiogenesis, the enhanced sensitivity of this developmental process to copper bioavailability has remained an enigma, because copper metalloproteins are prevalent and essential throughout all cells. Recent developments in x-ray optics at third-generation synchrotron sources have provided a resource for highly sensitive visualization and quantitation of metalloproteins in biological samples. Here, we report the application of x-ray fluorescence microscopy (XFM) toin vitro models of angiogenesis and neurogenesis, revealing a surprisingly dramatic spatial relocalization specific to capillary formation of 80-90% of endogenous cellular copper stores from intracellular compartments to the tips of nascent endothelial cell filopodia and across the cell membrane. Although copper chelation had no effect on process formation, an almost complete ablation of network formation was observed. XFM of highly vascularized ductal carcinomas showed copper clustering in putative neoangiogenic areas. This use of XFM for the study of a dynamic developmental process not only sheds light on the copper requirement for endothelial tube formation but highlights the value of synchrotron-based facilities in biological research.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
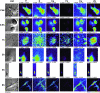
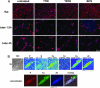
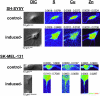
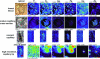
Similar articles
-
Copper and angiogenesis: unravelling a relationship key to cancer progression.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2009 Jan;36(1):88-94. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2008.04969.x. Epub 2008 May 23. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2009. PMID: 18505439 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synchrotron radiation X-ray fluorescence microscopy reveals a spatial association of copper on elastic laminae in rat aortic media.Metallomics. 2011 Aug;3(8):823-8. doi: 10.1039/c1mt00033k. Epub 2011 May 18. Metallomics. 2011. PMID: 21589993
-
[Extracellular matrix components and angiogenesis].Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 1996 Mar;107(3):153-60. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 1996. PMID: 8728288 Review. Japanese.
-
Reorganization of basement membrane matrices by cellular traction promotes the formation of cellular networks in vitro.Lab Invest. 1992 May;66(5):536-47. Lab Invest. 1992. PMID: 1374138
-
X-ray fluorescence microprobe imaging in biology and medicine.J Cell Biochem. 2006 Dec 15;99(6):1489-502. doi: 10.1002/jcb.21047. J Cell Biochem. 2006. PMID: 17006954 Review.
Cited by
-
Coordination Environment of Cu(II) Ions Bound to N-Terminal Peptide Fragments of Angiogenin Protein.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Aug 1;17(8):1240. doi: 10.3390/ijms17081240. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27490533 Free PMC article.
-
Demand for Zn2+ in acid-secreting gastric mucosa and its requirement for intracellular Ca2+.PLoS One. 2011;6(6):e19638. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0019638. Epub 2011 Jun 15. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21698273 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging trace element distributions in single organelles and subcellular features.Sci Rep. 2016 Feb 25;6:21437. doi: 10.1038/srep21437. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26911251 Free PMC article.
-
CD147 functions as the signaling receptor for extracellular divalent copper in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.Oncotarget. 2017 May 9;8(31):51151-51163. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17712. eCollection 2017 Aug 1. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28881637 Free PMC article.
-
β-Cell subcellular localization of glucose-stimulated Mn uptake by X-ray fluorescence microscopy: implications for pancreatic MRI.Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2011 Nov-Dec;6(6):474-81. doi: 10.1002/cmmi.447. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2011. PMID: 22144025 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lippard SJ, Berg JM. Principles of Bioinorganic Chemistry. Mill Valley, CA: Univ Sci Books; 1994.
-
- Valko M, Morris H, Cronin MT. Curr Med Chem. 2005;12:1161–1208. - PubMed
-
- O'Halloran TV, Culotta VC. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:25057–25060. - PubMed
-
- Finney LA, O'Halloran TV. Science. 2003;300:931–936. - PubMed
-
- Ziche M, Jones J, Gullino PM. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1982;69:475–482. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

