CAR and PXR: the xenobiotic-sensing receptors
- PMID: 17284330
- PMCID: PMC1950246
- DOI: 10.1016/j.steroids.2006.12.006
CAR and PXR: the xenobiotic-sensing receptors
Abstract
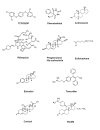
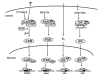
The xenobiotic receptors CAR and PXR constitute two important members of the NR1I nuclear receptor family. They function as sensors of toxic byproducts derived from endogenous metabolism and of exogenous chemicals, in order to enhance their elimination. This unique function of CAR and PXR sets them apart from the steroid hormone receptors. In contrast, the steroid receptors, exemplified by the estrogen receptor (ER) and glucocorticoid receptor (GR), are the sensors that tightly monitor and respond to changes in circulating steroid hormone levels to maintain body homeostasis. This divergence of the chemical- and steroid-sensing functions has evolved to ensure the fidelity of the steroid hormone endocrine regulation while allowing development of metabolic elimination pathways for xenobiotics. The development of the xenobiotic receptors CAR and PXR also reflect the increasing complexity of metabolism in higher organisms, which necessitate novel mechanisms for handling and eliminating metabolic by-products and foreign compounds from the body. The purpose of this review is to discuss similarities and differences between the xenobiotic receptors CAR and PXR with the prototypical steroid hormone receptors ER and GR. Interesting differences in structure explain in part the divergence in function and activation mechanisms of CAR/PXR from ER/GR. In addition, the physiological roles of CAR and PXR will be reviewed, with discussion of interactions of CAR and PXR with endocrine signaling pathways.
Figures


References
-
- Kodama S, Negishi M. Phenobarbital confers its diverse effects by activating the orphan nuclear receptor CAR. Drug Metab Rev. 2006;38:75–87. - PubMed
-
- Sueyoshi T, Negishi M. Phenobarbital response elements of cytochrome P450 genes and nuclear receptors. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2001;41:123–43. - PubMed
-
- Swales K, Kakizaki S, Yamamoto Y, Inoue K, Kobayashi K, Negishi M. Novel CAR-mediated mechanism for synergistic activation of two distinct elements within the human cytochrome P450 2B6 gene in HepG2 cells. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:3458–66. - PubMed
-
- Qatanani M, Zhang J, Moore DD. Role of the constitutive androstane receptor in xenobiotic-induced thyroid hormone metabolism. Endocrinology. 2005;146:995–1002. - PubMed
-
- Maglich JM, Watson J, McMillen PJ, Goodwin B, Willson TM, Moore JT. The nuclear receptor CAR is a regulator of thyroid hormone metabolism during caloric restriction. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:19832–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

