Eukaryotic RNase P RNA mediates cleavage in the absence of protein
- PMID: 17284611
- PMCID: PMC1892975
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0607326104
Eukaryotic RNase P RNA mediates cleavage in the absence of protein
Erratum in
- Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 May 12;106(19):8078
Abstract
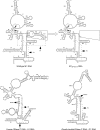
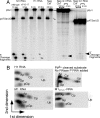
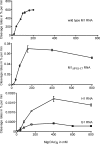
The universally conserved ribonucleoprotein RNase P is involved in the processing of tRNA precursor transcripts. RNase P consists of one RNA and, depending on its origin, a variable number of protein subunits. Catalytic activity of the RNA moiety so far has been demonstrated only for bacterial and some archaeal RNase P RNAs but not for their eukaryotic counterparts. Here, we show that RNase P RNAs from humans and the lower eukaryote Giardia lamblia mediate cleavage of four tRNA precursors and a model RNA hairpin loop substrate in the absence of protein. Compared with bacterial RNase P RNA, the rate of cleavage (k(obs)) was five to six orders of magnitude lower, whereas the affinity for the substrate (appK(d)) was reduced approximately 20- to 50-fold. We conclude that the RNA-based catalytic activity of RNase P has been preserved during evolution. This finding opens previously undescribed ways to study the role of the different proteins subunits of eukaryotic RNase P.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
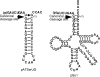
Comment in
-
Uniformity amid diversity in RNase P.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Feb 13;104(7):2031-2. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0611193104. Epub 2007 Feb 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17287341 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
RNase P RNA mediated cleavage: substrate recognition and catalysis.Biochimie. 2007 Oct;89(10):1183-94. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2007.05.009. Epub 2007 Jun 2. Biochimie. 2007. PMID: 17624654 Review.
-
Eukaryotic RNase P: role of RNA and protein subunits of a primordial catalytic ribonucleoprotein in RNA-based catalysis.Mol Cell. 2003 Oct;12(4):925-35. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(03)00357-5. Mol Cell. 2003. PMID: 14580343
-
Evidence for induced fit in bacterial RNase P RNA-mediated cleavage.J Mol Biol. 2007 Oct 5;372(5):1149-64. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2007.07.030. Epub 2007 Jul 29. J Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17719605
-
Substrate discrimination in RNase P RNA-mediated cleavage: importance of the structural environment of the RNase P cleavage site.Nucleic Acids Res. 2005 Apr 7;33(6):2012-21. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki344. Print 2005. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005. PMID: 15817565 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple structural flavors of RNase P in precursor tRNA processing.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2024 Mar-Apr;15(2):e1835. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1835. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2024. PMID: 38479802 Review.
Cited by
-
Interactions between subunits of Saccharomyces cerevisiae RNase MRP support a conserved eukaryotic RNase P/MRP architecture.Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(19):6439-50. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm553. Epub 2007 Sep 19. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007. PMID: 17881380 Free PMC article.
-
Minor changes largely restore catalytic activity of archaeal RNase P RNA from Methanothermobacter thermoautotrophicus.Nucleic Acids Res. 2009 Jan;37(1):231-42. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn915. Epub 2008 Nov 26. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009. PMID: 19036794 Free PMC article.
-
Cleavage mediated by the P15 domain of bacterial RNase P RNA.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Mar;40(5):2224-33. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr1001. Epub 2011 Nov 18. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22102593 Free PMC article.
-
The many faces of RNA-based RNase P, an RNA-world relic.Trends Biochem Sci. 2021 Dec;46(12):976-991. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2021.07.005. Epub 2021 Sep 9. Trends Biochem Sci. 2021. PMID: 34511335 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNase P-Mediated Sequence-Specific Cleavage of RNA by Engineered External Guide Sequences.Biomolecules. 2015 Nov 9;5(4):3029-50. doi: 10.3390/biom5043029. Biomolecules. 2015. PMID: 26569326 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

