Longitudinal changes in epitope recognition of autoantibodies against glutamate decarboxylase 65 (GAD65Ab) in prediabetic adults developing diabetes
- PMID: 17286757
- PMCID: PMC1868852
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2007.03334.x
Longitudinal changes in epitope recognition of autoantibodies against glutamate decarboxylase 65 (GAD65Ab) in prediabetic adults developing diabetes
Abstract
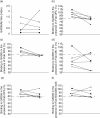
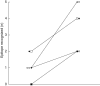
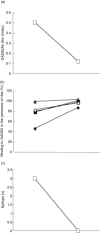
We analysed the beta cell-specific autoimmunity reflected in autoantibodies to the smaller isoform of glutamate decarboxylase (GAD65Ab) in the prediabetic period of GAD65Ab-positive healthy adults who developed Type 2 diabetes (T2D) during a follow-up period of 10 years. We found that of the adults that tested GAD65Ab-positive at baseline (n=25), six developed T2D and one developed Type 1 diabetes (T1D). Of the subjects that tested GAD65Ab-negative at baseline (n=2209), 81 developed T2D, one developed T1D and four developed unclassified diabetes, indicating that the risk for GAD65Ab-positive healthy adults to develop diabetes is increased sixfold. The GAD65Ab epitopes were characterized in a competition radioligand binding assay using recombinant Fab derived of GAD65-specific monoclonal antibodies. We observed that the GAD65Ab epitope specificities in the prediabetic period changed dynamically. Specifically, the binding to a middle and a C-terminal epitope increased during the follow-up period (P=0 x 03), causing a significant increase in the number of epitopes recognized (P=0 x 03). These findings are similar to previous observations of dynamic changes in the prediabetic period of schoolchildren at high risk for T1D development. However, the character of the epitopes differs between the two populations, suggesting differences in the beta cell-specific autoimmune response in the prediabetic period of patients with latent autoimmune diabetes in adults (LADA) and T1D.
Figures

References
-
- Bingley PJ, Christie MR, Bonifacio E, et al. Combined analysis of autoantibodies improves prediction of IDDM in islet cell antibody-positive relatives. Diabetes. 1994;43:1304–10. - PubMed
-
- Kulmala P, Rahko J, Savola K, et al. Stability of autoantibodies and their relation to genetic and metabolic markers of Type I diabetes in initially unaffected schoolchildren. Diabetologia. 2000;43:457–64. - PubMed
-
- Graham J, Hagopian WA, Kockum I, et al. Genetic effects on age-dependent onset and islet cell autoantibody markers in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes. 2002;51:1346–55. - PubMed
-
- Groop LC, Bottazzo GF, Doniac D. Islet cell antibodies identify latent type 1 diabetes in patients aged 35–75 years at diagnosis. Diabetes. 1986;35:237–41. - PubMed
-
- Rowley MJ, Mackay IR, Chen QY, Knowles WJ, Zimmet PZ. Antibodies to glutamic acid decarboxylase discriminate major types of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1992;41:548–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

