PlnTFDB: an integrative plant transcription factor database
- PMID: 17286856
- PMCID: PMC1802092
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-8-42
PlnTFDB: an integrative plant transcription factor database
Abstract
Background: Transcription factors (TFs) are key regulatory proteins that enhance or repress the transcriptional rate of their target genes by binding to specific promoter regions (i.e. cis-acting elements) upon activation or de-activation of upstream signaling cascades. TFs thus constitute master control elements of dynamic transcriptional networks. TFs have fundamental roles in almost all biological processes (development, growth and response to environmental factors) and it is assumed that they play immensely important functions in the evolution of species. In plants, TFs have been employed to manipulate various types of metabolic, developmental and stress response pathways. Cross-species comparison and identification of regulatory modules and hence TFs is thought to become increasingly important for the rational design of new plant biomass. Up to now, however, no computational repository is available that provides access to the largely complete sets of transcription factors of sequenced plant genomes.
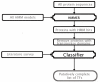
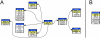
Description: PlnTFDB is an integrative plant transcription factor database that provides a web interface to access large (close to complete) sets of transcription factors of several plant species, currently encompassing Arabidopsis thaliana (thale cress), Populus trichocarpa (poplar), Oryza sativa (rice), Chlamydomonas reinhardtii and Ostreococcus tauri. It also provides an access point to its daughter databases of a species-centered representation of transcription factors (OstreoTFDB, ChlamyTFDB, ArabTFDB, PoplarTFDB and RiceTFDB). Information including protein sequences, coding regions, genomic sequences, expressed sequence tags (ESTs), domain architecture and scientific literature is provided for each family.
Conclusion: We have created lists of putatively complete sets of transcription factors and other transcriptional regulators for five plant genomes. They are publicly available through http://plntfdb.bio.uni-potsdam.de. Further data will be included in the future when the sequences of other plant genomes become available.
Figures
References
-
- Matys V, Kel-Margoulis OV, Pricke E, Liebich I, Land S, Barre-Dirrie A, Reuter I, Chekmenev D, Krull M, Hornischer K, Voss N, Stegmaier P, Lewicki-Potapov B, Saxel H, Kel AE, Wingender E. TRANSFAC and its module TRANSCompel: transcriptional gene regulation in eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006:D108–D110. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkj143. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

