APP-BP1 inhibits Abeta42 levels by interacting with Presenilin-1
- PMID: 17286867
- PMCID: PMC1802080
- DOI: 10.1186/1750-1326-2-3
APP-BP1 inhibits Abeta42 levels by interacting with Presenilin-1
Abstract
Background: The beta-amyloid precursor protein (APP) is sequentially cleaved by the beta- and then gamma-secretase to generate the amyloid beta-peptides Abeta40 and Abeta42. Increased Abeta42/Abeta40 ratios trigger amyloid plaque formations in Alzheimer's disease (AD). APP binds to APP-BP1, but the biological consequence is not well understood.
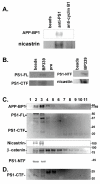
Results: We report that when the endogenous APP-BP1 was suppressed by small interfering RNAs (siRNAs), cell-associated Abeta42 was dramatically increased in APP695 expressing primary neurons. The accumulation of Abeta42 was accompanied by significant increases in APP and APP-CTF in APP-BP1 siRNA expressing neurons. In contrast, APP-BP1 overexpression in primary neurons significantly decreased the levels of Abeta and endogenous APP but not APLPs. We also investigated the potential mechanism of APP-BP1-mediated APP processing. APP-BP1 co-precipitated with Presenilin-1 (PS1) in native rat brain extracts, co-migrated with the gamma-secretase components in brain membrane extracts in glycerol gradient centrifugation, and colocalized in primary neurons. Further, the endogenous PS1-CTF was significantly downregulated by APP-BP1 expression.
Conclusion: Our data suggest that APP-BP1 may inhibit Abeta42 production by interacting with PS1 under physiological conditions.
Figures






References
-
- Wu JT, Lin HC, Hu YC, Chien CT. Neddylation and deneddylation regulate Cul1 and Cul3 protein accumulation. Nat Cell Biol. 2005. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

