TopBP1 regulates human papillomavirus type 16 E2 interaction with chromatin
- PMID: 17287259
- PMCID: PMC1866123
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02353-06
TopBP1 regulates human papillomavirus type 16 E2 interaction with chromatin
Abstract
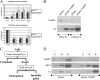
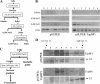
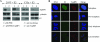
Human papillomavirus type 16 (HPV16) E2 regulates transcription from and replication of the viral genome, in association with viral and cellular factors. HPV16 E2 interacts functionally with TopBP1, a cellular protein essential for the initiation of cellular, and potentially viral, DNA replication. This report demonstrates that the absence of TopBP1 results in the redistribution of HPV16 E2 into an alternative cellular protein complex, resulting in enhanced affinity for chromatin. This redistribution does not significantly alter the ability of HPV16 E2 to either activate or repress transcription. We also show colocalization of both proteins on chromatin at late stages of mitosis, suggesting that TopBP1 could be the mitotic chromatin receptor for HPV16 E2. The possible significance of the results for the regulation of the viral life cycle is discussed.
Figures

References
-
- Boner, W., and I. M. Morgan. 2002. Novel cellular interacting partners of the human papillomavirus 16 transcription/replication factor E2. Virus Res. 90:113-118. - PubMed
-
- Boner, W., E. R. Taylor, E. Tsirimonaki, K. Yamane, M. S. Campo, and I. M. Morgan. 2002. A functional interaction between the human papillomavirus 16 transcription/replication factor E2 and the DNA damage response protein TopBP1. J. Biol. Chem. 277:22297-22303. - PubMed
-
- Ham, J., N. Dostatni, J. M. Gauthier, and M. Yaniv. 1991. The papillomavirus E2 protein: a factor with many talents. Trends Biochem. Sci. 16:440-444. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

