Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus induces sustained NF-kappaB activation during de novo infection of primary human dermal microvascular endothelial cells that is essential for viral gene expression
- PMID: 17287275
- PMCID: PMC1866142
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02333-06
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus induces sustained NF-kappaB activation during de novo infection of primary human dermal microvascular endothelial cells that is essential for viral gene expression
Abstract
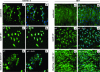
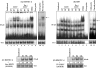
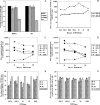
In vitro Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) infection of primary human dermal microvascular endothelial (HMVEC-d) cells and human foreskin fibroblast (HFF) cells is characterized by the induction of preexisting host signal cascades, sustained expression of latency-associated genes, transient expression of a limited number of lytic genes, and induction of several cytokines, growth factors, and angiogenic factors. Since NF-kappaB is a key molecule involved in the regulation of several of these factors, here, we examined NF-kappaB induction during de novo infection of HMVEC-d and HFF cells. Activation of NF-kappaB was observed as early as 5 to 15 min postinfection by KSHV, and translocation of p65-NF-kappaB into nuclei was detected by immunofluorescence assay, electrophoretic mobility shift assay, and p65 enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. IkappaB phosphorylation inhibitor (Bay11-7082) reduced this activation significantly. A sustained moderate level of NF-kappaB induction was seen during the observed 72 h of in vitro KSHV latency. In contrast, high levels of ERK1/2 activation at earlier time points and a moderate level of activation at later times were observed. p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase was activated only at later time points, and AKT was activated in a cyclic manner. Studies with UV-inactivated KSHV suggested a role for virus entry stages in NF-kappaB induction and a requirement for KSHV viral gene expression in sustained induction. Inhibition of NF-kappaB did not affect target cell entry by KSHV but significantly reduced the expression of viral latent open reading frame 73 and lytic genes. KSHV infection induced the activation of several host transcription factors, including AP-1 family members, as well as several cytokines, growth factors, and angiogenic factors, which were significantly affected by NF-kappaB inhibition. These results suggest that during de novo infection, KSHV induces sustained levels of NF-kappaB to regulate viral and host cell genes and thus possibly regulates the establishment of latent infection.
Figures
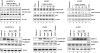





Similar articles
-
Interaction of KSHV with host cell surface receptors and cell entry.Viruses. 2014 Oct 23;6(10):4024-46. doi: 10.3390/v6104024. Viruses. 2014. PMID: 25341665 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ERK1/2 and MEK1/2 induced by Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (human herpesvirus 8) early during infection of target cells are essential for expression of viral genes and for establishment of infection.J Virol. 2005 Aug;79(16):10308-29. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.16.10308-10329.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 16051824 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclooxygenase 2 induced by Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus early during in vitro infection of target cells plays a role in the maintenance of latent viral gene expression.J Virol. 2006 Jul;80(13):6534-52. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00231-06. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16775340 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid rafts of primary endothelial cells are essential for Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus/human herpesvirus 8-induced phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and RhoA-GTPases critical for microtubule dynamics and nuclear delivery of viral DNA but dispensable for binding and entry.J Virol. 2007 Aug;81(15):7941-59. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02848-06. Epub 2007 May 16. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17507466 Free PMC article.
-
KSHV Entry and Trafficking in Target Cells-Hijacking of Cell Signal Pathways, Actin and Membrane Dynamics.Viruses. 2016 Nov 14;8(11):305. doi: 10.3390/v8110305. Viruses. 2016. PMID: 27854239 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Genome Replication, Partitioning, and Maintenance in Latency.Front Microbiol. 2012 Jan 24;3:7. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2012.00007. eCollection 2012. Front Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22291692 Free PMC article.
-
Robust inference of the context specific structure and temporal dynamics of gene regulatory network.BMC Genomics. 2010 Dec 1;11 Suppl 3(Suppl 3):S11. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-S3-S11. BMC Genomics. 2010. PMID: 21143778 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of KSHV with host cell surface receptors and cell entry.Viruses. 2014 Oct 23;6(10):4024-46. doi: 10.3390/v6104024. Viruses. 2014. PMID: 25341665 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Induction of CCL20 production by Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus: role of viral FLICE inhibitory protein K13-induced NF-kappaB activation.Blood. 2009 May 28;113(22):5660-8. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-10-186403. Epub 2009 Mar 26. Blood. 2009. PMID: 19324905 Free PMC article.
-
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) utilizes the NDP52/CALCOCO2 selective autophagy receptor to disassemble processing bodies.PLoS Pathog. 2023 Jan 12;19(1):e1011080. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1011080. eCollection 2023 Jan. PLoS Pathog. 2023. PMID: 36634147 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akula, S. M., N. P. Pramod, F. Z. Wang, and B. Chandran. 2001. Human herpesvirus 8 envelope-associated glycoprotein B interacts with heparan sulfate-like moieties. Virology 284:235-249. - PubMed
-
- Akula, S. M., F. Z. Wang, J. Vieira, and B. Chandran. 2001. Human herpesvirus 8 interaction with target cells involves heparan sulfate. Virology 282:245-255. - PubMed
-
- An, J., A. K. Lichtenstein, G. Brent, and M. B. Rettig. 2002. The Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) induces cellular interleukin 6 expression: role of the KSHV latency-associated nuclear antigen and the AP1 response element. Blood 99:649-654. - PubMed
-
- An, J., Y. Sun, R. Sun, and M. B. Rettig. 2003. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus encoded vFLIP induces cellular IL-6 expression: the role of the NF-κB and JNK/AP1 pathways. Oncogene 22:3371-3385. - PubMed
-
- Baeuerle, P. A., and D. Baltimore. 1996. NF-kappa B: ten years after. Cell 87:13-20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

