Milk of cow (Bos taurus), buffalo (Bubalus bubalis), and goat (Capra hircus): a better alternative than fetal bovine serum in media for primary isolation, in vitro cultivation, and maintenance of Leishmania donovani promastigotes
- PMID: 17287321
- PMCID: PMC1865826
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.01761-06
Milk of cow (Bos taurus), buffalo (Bubalus bubalis), and goat (Capra hircus): a better alternative than fetal bovine serum in media for primary isolation, in vitro cultivation, and maintenance of Leishmania donovani promastigotes
Abstract
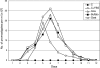
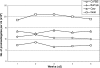
Tyndalized milk of goat, cow, and buffalo was found to be a potential substitute for fetal bovine serum (FBS) in the medium for the cultivation of Leishmania donovani promastigotes. The numbers (means) of promastigotes reached 2.6 x 10(7), 2.3 x 10(7), and 2.1 x 10(7)/ml, respectively, in the medium supplemented with 10% milk of goat, cow, and buffalo, in comparison to 1.9 x 10(7)/ml in the control with 10% FBS. In primary isolation, the milk-supplemented medium showed that 22 out of 26 samples were positive for promastigotes (84.6%) and the cells were maintained successfully during the observed period of 6 months.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Use of modified Grace's insect medium for the primary isolation of Leishmania donovani donovani in Bihar, India.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1986 May;35(3):488-90. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1986.35.488. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1986. PMID: 3706619
-
A simple medium without blood modified for successful isolation & cultivation of LD bodies.Indian J Med Res. 1994 Apr;99:171-2. Indian J Med Res. 1994. PMID: 7927570
-
New blood free biphasic medium with haemoglobin for cultivation of Leishmania donovani promastigotes.Indian J Exp Biol. 1996 Dec;34(12):1233-6. Indian J Exp Biol. 1996. PMID: 9246917
-
Animal reservoirs of visceral leishmaniasis in India.J Parasitol. 2013 Feb;99(1):64-7. doi: 10.1645/GE-3085.1. Epub 2012 Jul 5. J Parasitol. 2013. PMID: 22765517
-
Goat serum: an alternative to fetal bovine serum in biomedical research.Indian J Exp Biol. 2004 Jan;42(1):26-35. Indian J Exp Biol. 2004. PMID: 15274477 Review.
Cited by
-
Leishmania Parasite: the Impact of New Serum-Free Medium as an Alternative for Fetal Bovine Serum.Iran Biomed J. 2021 Sep 1;25(5):349-58. doi: 10.52547/ibj.25.5.349. Epub 2021 Aug 29. Iran Biomed J. 2021. PMID: 34481426 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of camel, dog and the laboratory animals' sera with the fetal calf serum (FCS) for cultivation of Leishmania major.J Parasit Dis. 2020 Jun;44(2):299-304. doi: 10.1007/s12639-020-01203-x. Epub 2020 Feb 8. J Parasit Dis. 2020. PMID: 32508404 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Eight Cell-Free Media for Maintenance of Toxoplasma gondii Tachyzoites.Iran J Parasitol. 2016 Jan-Mar;11(1):104-9. Iran J Parasitol. 2016. PMID: 27095976 Free PMC article.
-
A new experimental culture medium for cultivation of Leishmania amazonensis: its efficacy for the continuous in vitro growth and differentiation of infective promastigote forms.Parasitol Res. 2010 Apr;106(5):1249-52. doi: 10.1007/s00436-010-1775-4. Epub 2010 Feb 23. Parasitol Res. 2010. PMID: 20177905
References
-
- Ali, S. A., J. Iqbal, B. Ahmad, and M. Masoom. 1998. A semi synthetic fetal calf serum-free liquid medium for in vitro cultivation of Leishmania promastigotes. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 59:163-165. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong, T. C., and J. L. Patterson. 1994. Cultivation of Leishmania braziliensis in an economical serum-free medium containing human urine. J. Parasitol. 80:1030-1032. - PubMed
-
- Chaudhuri, G., K. Ghoshal, S. Sen, S. Pal., and A. B. Banerjee. 1986. Nutrition of Leishmania donovani donovani: growth in new semidefined & completely chemically defined media. Indian J. Med. Res. 84:461-468. - PubMed
-
- Cullimore, D. R., and N. Mansuy. 1986. The control of iron bacteria plugging of a well by tyndalization using hot water recycling. Water Pollut. Res. J. Can. 21:50-57.
-
- Reference deleted.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

