Pharmacological inhibition of glucosylceramide synthase enhances insulin sensitivity
- PMID: 17287460
- PMCID: PMC4298701
- DOI: 10.2337/db06-1619
Pharmacological inhibition of glucosylceramide synthase enhances insulin sensitivity
Abstract
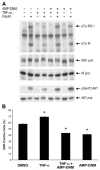
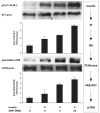
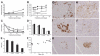
A growing body of evidence implicates ceramide and/or its glycosphingolipid metabolites in the pathogenesis of insulin resistance. We have developed a highly specific small molecule inhibitor of glucosylceramide synthase, an enzyme that catalyzes a necessary step in the conversion of ceramide to glycosphingolipids. In cultured 3T3-L1 adipocytes, the iminosugar derivative N-(5'-adamantane-1'-yl-methoxy)-pentyl-1-deoxynojirimycin (AMP-DNM) counteracted tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced abnormalities in glycosphingolipid concentrations and concomitantly reversed abnormalities in insulin signal transduction. When administered to mice and rats, AMP-DNM significantly reduced glycosphingolipid but not ceramide concentrations in various tissues. Treatment of ob/ob mice with AMP-DNM normalized their elevated tissue glucosylceramide levels, markedly lowered circulating glucose levels, improved oral glucose tolerance, reduced A1C, and improved insulin sensitivity in muscle and liver. Similarly beneficial metabolic effects were seen in high fat-fed mice and ZDF rats. These findings provide further evidence that glycosphingolipid metabolites of ceramide may be involved in mediating the link between obesity and insulin resistance and that interference with glycosphingolipid biosynthesis might present a novel approach to the therapy of states of impaired insulin action such as type 2 diabetes.
Figures


References
-
- Unger RH. Minireview: weapons of lean body mass destruction: the role of ectopic lipids in the metabolic syndrome. Endocrinology. 2003;144:5159–5165. - PubMed
-
- Savage DB, Petersen KF, Shulman GI. Mechanisms of insulin resistance in humans and possible links with inflammation. Hypertension. 2005;45:828–833. - PubMed
-
- Hegarty BD, Furler SM, Ye J, Cooney GJ, Kraegen EW. The role of intramuscular lipid in insulin resistance. Acta Physiol Scand. 2003;178:373–383. - PubMed
-
- Adams JM, 2nd, Pratipanawatr T, Berria R, Wang E, DeFronzo RA, Sullards MC, Mandarino LJ. Ceramide content is increased in skeletal muscle from obese insulin-resistant humans. Diabetes. 2004;53:25–31. - PubMed
-
- Summers SA. Ceramides in insulin resistance and lipotoxicity. Prog Lipid Res. 2006;45:42–72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

