Presynaptic alpha-synuclein aggregates, not Lewy bodies, cause neurodegeneration in dementia with Lewy bodies
- PMID: 17287515
- PMCID: PMC6673583
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4564-06.2007
Presynaptic alpha-synuclein aggregates, not Lewy bodies, cause neurodegeneration in dementia with Lewy bodies
Abstract
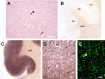
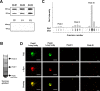
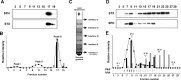
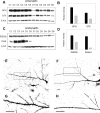
Lewy bodies, the pathological hallmark of dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB), are large juxtanuclear inclusions of aggregated alpha-synuclein. However, the small number of cortical Lewy bodies relative to the total neuron count does not correlate with the extent of cognitive impairment. In contrast to dopaminergic neurons in Parkinson's disease, nerve cell loss is usually less prevalent in the cortex of DLB, suggesting a different mechanism of neurodegeneration. Because antibodies used for immunodetection per se do not generally differentiate the aggregated from the physiological and monomeric isoform of alpha-synuclein, we developed the paraffin-embedded tissue (PET) blot and the protein aggregate filtration (PAF) assay for the sensitive and selective detection of alpha-synuclein aggregates in tissue slides and brain homogenates, respectively. In contrast to common immunohistochemistry, the PET blot detected an enormous number of small alpha-synuclein aggregates, which, in contrast to the few Lewy bodies, may explain the cognitive impairment in DLB. Using the PAF assay, we demonstrate that the absolute majority of alpha-synuclein aggregates are located at presynaptic terminals, suggesting a severe pathological impact on synaptic function. Indeed, parallel to the massive presynaptic accumulation of alpha-synuclein aggregates, we observed significant synaptic pathology with almost complete loss of dendritic spines at the postsynaptic area. Our results provide strong evidence for a novel concept of neurodegeneration for DLB in which synaptic dysfunction is caused by presynaptic accumulation of alpha-synuclein aggregates. This concept may also be valid for Parkinson's disease.
Figures
References
-
- Chandra S, Gallardo G, Fernandez-Chacon R, Schluter OM, Sudhof TC. Alpha-synuclein cooperates with CSPalpha in preventing neurodegeneration. Cell. 2005;123:383–396. - PubMed
-
- Dodd PR, Watson WE, Morrison MM, Johnston GA, Bird ED, Cowburn RF, Hardy JA. Uptake of gamma-aminobutyric acid and l-glutamic acid by synaptosomes from postmortem human cerebral cortex: multiple sites, sodium dependence and effect of tissue preparation. Brain Res. 1989;490:320–331. - PubMed
-
- Engert F, Bonhoeffer T. Dendritic spine changes associated with hippocampal long-term synaptic plasticity. Nature. 1999;399:66–70. - PubMed
-
- Fujiwara H, Hasegawa M, Dohmae N, Kawashima A, Masliah E, Goldberg MS, Shen J, Takio K, Iwatsubo T. Alpha-synuclein is phosphorylated in synucleinopathy lesions. Nat Cell Biol. 2002;4:160–164. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
