Estrogen regulates Bcl-w and Bim expression: role in protection against beta-amyloid peptide-induced neuronal death
- PMID: 17287517
- PMCID: PMC6673600
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2382-06.2007
Estrogen regulates Bcl-w and Bim expression: role in protection against beta-amyloid peptide-induced neuronal death
Abstract
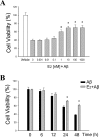
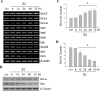
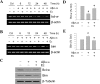
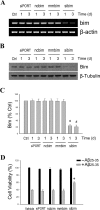
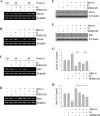
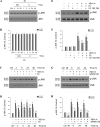
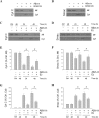
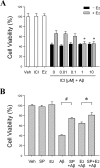
Estrogen is neuroprotective against a variety of insults, including beta-amyloid peptide (Abeta); however, the underlying mechanism(s) is not fully understood. Here, we report that 17beta-estradiol (E2) selectively regulates neuronal expression of the Bcl-2 family (bcl-2, bcl-x, bcl-w, bax, bak, bad, bik, bnip3, bid, and bim). In primary cerebrocortical neuron cultures under basal conditions, we observe that E2 upregulates expression of antiapoptotic Bcl-w and downregulates expression of proapoptotic Bim in an estrogen receptor (ER)-dependent manner. In the presence of toxic levels of Abeta, we observe that E2 attenuates indices of neuronal apoptosis: c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK)-dependent downregulation of Bcl-w and upregulation of Bim, mitochondrial release of cytochrome c and Smac, and cell death. These neuroprotective effects of E2 against Abeta-induced apoptosis are mimicked by the JNK inhibitor SP600125 (anthra[1,9-cd]pyrazol-6(2H)-one). In addition, E2 attenuates Abeta-induced JNK phosphorylation in an ER-dependent manner, but does not affect basal levels of JNK phosphorylation. These results suggest that E2 may reduce Abeta-induced neuronal apoptosis at least in part by two complementary pathways: (1) ER-dependent, JNK-independent upregulation of Bcl-w and downregulation of Bim under basal conditions, and (2) ER-dependent inhibition of Abeta-induced JNK activation and subsequent JNK-dependent downregulation of Bcl-w and upregulation of Bim, resulting in mitochondrial release of cytochrome c and Smac and eventual cell death. These data provide new understanding into the mechanisms contributing to estrogen neuroprotection, a neural function with potential therapeutic relevance to Alzheimer's disease.
Figures

References
-
- Agostinho P, Oliveira CR. Involvement of calcineurin in the neurotoxic effects induced by amyloid-beta and prion peptides. Eur J Neurosci. 2003;17:1189–1196. - PubMed
-
- Ahlbom E, Prins GS, Ceccatelli S. Testosterone protects cerebellar granule cells from oxidative stress-induced cell death through a receptor mediated mechanism. Brain Res. 2001;892:255–262. - PubMed
-
- Antonsson B, Martinou JC. The Bcl-2 protein family. Exp Cell Res. 2000;256:50–57. - PubMed
-
- Bae MA, Song BJ. Critical role of c-Jun N-terminal protein kinase activation in troglitazone-induced apoptosis of human HepG2 hepatoma cells. Mol Pharmacol. 2003;63:401–408. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
