Improved precision and accuracy for microarrays using updated probe set definitions
- PMID: 17288599
- PMCID: PMC1805763
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-8-48
Improved precision and accuracy for microarrays using updated probe set definitions
Abstract
Background: Microarrays enable high throughput detection of transcript expression levels. Different investigators have recently introduced updated probe set definitions to more accurately map probes to our current knowledge of genes and transcripts.
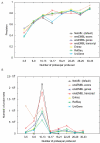
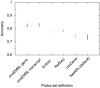
Results: We demonstrate that updated probe set definitions provide both better precision and accuracy in probe set estimates compared to the original Affymetrix definitions. We show that the improved precision mainly depends on the increased number of probes that are integrated into each probe set, but we also demonstrate an improvement when the same number of probes is used.
Conclusion: Updated probe set definitions does not only offer expression levels that are more accurately associated to genes and transcripts but also improvements in the estimated transcript expression levels. These results give support for the use of updated probe set definitions for analysis and meta-analysis of microarray data.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

