Asymmetry of syringomycin E channel studied by polymer partitioning
- PMID: 17289034
- PMCID: PMC1866293
- DOI: 10.1016/j.febslet.2007.01.063
Asymmetry of syringomycin E channel studied by polymer partitioning
Abstract
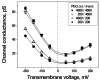
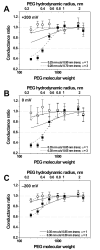
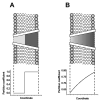
To probe the size of the ion channel formed by Pseudomonas syringae lipodepsipeptide syringomycin E, we use the partial blockage of ion current by penetrating poly(ethylene glycol)s. Earlier experiments with symmetric application of these polymers yielded a radius estimate of approximately 1 nm. Now, motivated by the asymmetric non-ohmic current-voltage curves reported for this channel, we explore its structural asymmetry. We gauge this asymmetry by studying the channel conductance after one-sided addition of differently sized poly(ethylene glycol)s. We find that small polymers added to the cis-side of the membrane (the side of lipodepsipeptide addition) reduce channel conductance much less than do the same polymers added to the trans-side. We interpret our results to suggest that the water-filled pore of the channel is conical with cis- and trans-radii differing by a factor of 2-3 and that the smaller cis-radius is in the 0.25-0.35 nm range. In symmetric, two-sided addition, polymers entering the pore from the larger opening dominate blockage.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cluster organization of ion channels formed by the antibiotic syringomycin E in bilayer lipid membranes.Biophys J. 1998 Jun;74(6):2918-25. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(98)77999-8. Biophys J. 1998. PMID: 9635746 Free PMC article.
-
Polymeric nonelectrolytes to probe pore geometry: application to the alpha-toxin transmembrane channel.Biophys J. 1999 Dec;77(6):3023-33. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(99)77133-X. Biophys J. 1999. PMID: 10585924 Free PMC article.
-
[Kinetic parameters of single ion channels and stationary conductivities of phytotoxin modified lipid bilayers].Tsitologiia. 2005;47(4):338-43. Tsitologiia. 2005. PMID: 16706157 Russian.
-
Actin and amphiphilic polymers influence on channel formation by Syringomycin E in lipid bilayers.Eur Biophys J. 2006 May;35(5):382-92. doi: 10.1007/s00249-006-0045-y. Epub 2006 Feb 10. Eur Biophys J. 2006. PMID: 16470378
-
Probing protein nanopores with poly(ethylene glycol)s.Proteomics. 2022 Mar;22(5-6):e2100055. doi: 10.1002/pmic.202100055. Epub 2022 Jan 24. Proteomics. 2022. PMID: 35030301 Review.
Cited by
-
Two types of syringomycin E channels in sphingomyelin-containing bilayers.Eur Biophys J. 2016 Jan;45(1):91-8. doi: 10.1007/s00249-015-1101-2. Epub 2015 Dec 11. Eur Biophys J. 2016. PMID: 26658744
-
Modulation of the Dipole Potential of Model Lipid Membranes with Phytochemicals: Molecular Mechanisms, Structure-Activity Relationships, and Implications in Reconstituted Ion Channels.Membranes (Basel). 2023 Apr 21;13(4):453. doi: 10.3390/membranes13040453. Membranes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37103880 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ion Channels Induced by Antimicrobial Agents in Model Lipid Membranes are Modulated by Plant Polyphenols Through Surrounding Lipid Media.J Membr Biol. 2018 Aug;251(4):551-562. doi: 10.1007/s00232-018-0031-1. Epub 2018 Mar 16. J Membr Biol. 2018. PMID: 29549386
-
Lipid-Centric Approaches in Combating Infectious Diseases: Antibacterials, Antifungals and Antivirals with Lipid-Associated Mechanisms of Action.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Dec 11;12(12):1716. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12121716. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38136750 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Is the Membrane Lipid Matrix a Key Target for Action of Pharmacologically Active Plant Saponins?Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 20;22(6):3167. doi: 10.3390/ijms22063167. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33804648 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Feigin AM, Takemoto JY, Wangspa R, Teeter JH, Brand JG. Properties of voltage-gated ion channels formed by syringomycin E in planar lipid bilayers. J Membr Biol. 1996;149:41–47. - PubMed
-
- Schagina LV, Kaulin YA, Feigin AM, Takemoto JY, Brand JG, Malev VV. Properties of ionic channels formed by the antibiotic syringomycin E in lipid bilayers: dependence on the electrolyte concentration in the bathing solution. Membr Cell Biol. 1998;12:537–555. - PubMed
-
- Zimmerberg J, Parsegian VA. Polymer inaccessible volume changes during opening and closing of a voltage-dependent ionic channel. Nature. 1986;323:36–39. - PubMed
-
- Krasilnikov OV, Sabirov RZ, Ternovsky VI, Merzliak PG, Muratkhodjaev JN. A simple method for the determination of the pore radius of ion channels in planar lipid bilayer membranes. FEMS Microbiol Immunol. 1992;5:93–100. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

