Hypothalamic and hindbrain NPY, AGRP and NE increase consummatory feeding responses
- PMID: 17289093
- PMCID: PMC2706100
- DOI: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2006.12.014
Hypothalamic and hindbrain NPY, AGRP and NE increase consummatory feeding responses
Abstract
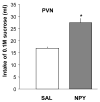
Feeding behavior is comprised of both appetitive and consummatory responses to food. Appetitive responses include the motivated acquisition of food. Consummatory responses, including swallowing, are those that move the food from the mouth to the stomach. Intraoral delivery of liquid food bypasses the requirement for appetitive responses and has been used to examine consummatory responses directly in intact rats. In the present study, we administered neuropeptide Y (NPY), agouti-related protein (AGRP) and norepinephrine (NE), into the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus (PVN) or into the fourth cerebral ventricle to examine their effects on the consummatory component of feeding behavior in the rat. To measure consummatory responses, milk (40% lactose free cow's milk diluted with water) was infused intraorally through a chronic cheek fistula (1 ml/min), using an alternating 5 min on -1 min off schedule, until rejection occurred. We found that both hypothalamic and fourth ventricle injections of NPY, AGRP and NE significantly increased consumption of the intraorally-delivered milk. Our results indicate that the circuitry for modulation of consummatory ingestive responses includes NE, NPY and AGRP receptors operating in both hypothalamic and hindbrain sites.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Hindbrain catecholamine neurons mediate consummatory responses to glucoprivation.Physiol Behav. 2004 Sep 15;82(2-3):241-50. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2004.03.032. Physiol Behav. 2004. PMID: 15276785
-
A role for agouti-related protein in appetite regulation in a species with continuous nutrient delivery.Neuroendocrinology. 2004;80(4):210-8. doi: 10.1159/000082735. Epub 2004 Dec 13. Neuroendocrinology. 2004. PMID: 15604600
-
Immunolesion of norepinephrine and epinephrine afferents to medial hypothalamus alters basal and 2-deoxy-D-glucose-induced neuropeptide Y and agouti gene-related protein messenger ribonucleic acid expression in the arcuate nucleus.Endocrinology. 2003 Jan;144(1):75-83. doi: 10.1210/en.2002-220659. Endocrinology. 2003. PMID: 12488332
-
Hindbrain catecholamine neurons control multiple glucoregulatory responses.Physiol Behav. 2006 Nov 30;89(4):490-500. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2006.05.036. Epub 2006 Aug 1. Physiol Behav. 2006. PMID: 16887153 Review.
-
Neuroendocrine actions and regulation of hypothalamic neuropeptide Y during lactation.Peptides. 2007 Feb;28(2):447-52. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2006.09.025. Epub 2007 Jan 22. Peptides. 2007. PMID: 17241697 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 is required in hypothalamic agouti-related protein/neuropeptide Y neurons for normal energy homeostasis.Endocrinology. 2008 Jul;149(7):3346-54. doi: 10.1210/en.2007-0945. Epub 2008 Apr 10. Endocrinology. 2008. PMID: 18403487 Free PMC article.
-
Administration of IL-1beta to the 4th ventricle causes anorexia that is blocked by agouti-related peptide and that coincides with activation of tyrosine-hydroxylase neurons in the nucleus of the solitary tract.Peptides. 2009 Feb;30(2):210-8. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2008.10.019. Epub 2008 Nov 5. Peptides. 2009. PMID: 19028534 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of NPY receptors suppresses excitatory synaptic transmission in a taste-feeding network in the lower brain stem.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2012 Jun 15;302(12):R1401-10. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00536.2011. Epub 2012 Apr 18. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22513746 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in food intake and glucosensing function of hypothalamus and hindbrain in rainbow trout subjected to hyperglycemic or hypoglycemic conditions.J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol. 2008 Sep;194(9):829-39. doi: 10.1007/s00359-008-0354-y. Epub 2008 Jul 29. J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18663455
-
Orexin-A enhances feeding in male rats by activating hindbrain catecholamine neurons.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2015 Aug 15;309(4):R358-67. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00065.2015. Epub 2015 Jun 10. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26062632 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Grill HJ. Caudal brainstem contributions to the integrated neural control of energy homeostasis. In: Ritter RC, Ritter S, Barnes CD, editors. Feeding behavior: Neural and humoral controls. Orlando: Academic Press; 1986. pp. 102–29.
-
- Cunningham ET, Jr, Sawchenko PE. Dorsal medullary pathways subserving oromotor reflexes in the rat: Implications for the central neural control of swallowing. J Comp Neurol. 2000;417:448–66. - PubMed
-
- Amirali A, Tsai G, Schrader N, Weisz D, Sanders I. Mapping of brain stem neuronal circuitry active during swallowing. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2001;110:502–13. - PubMed
-
- Grill HJ. Production and regulation of ingestive consummatory behavior in the chronic decerebrate rat. Brain Res Bull. 1980;5:79–87.
-
- Hudson B, Ritter S. Hindbrain catecholamine neurons mediate consummatory responses to glucoprivation. Physiol Behav. 2004;82:241–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

