Inhibition of G alpha i2 activation by G alpha i3 in CXCR3-mediated signaling
- PMID: 17289675
- PMCID: PMC2366813
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M610931200
Inhibition of G alpha i2 activation by G alpha i3 in CXCR3-mediated signaling
Abstract
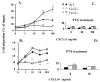
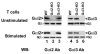
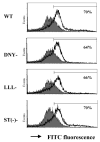
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) convey extracellular stimulation into dynamic intracellular action, leading to the regulation of cell migration and differentiation. T lymphocytes express G alpha(i2) and G alpha(i3), two members of the G alpha(i/o) protein family, but whether these two G alpha(i) proteins have distinguishable roles guiding T cell migration remains largely unknown because of a lack of member-specific inhibitors. This study details distinct G alpha(i2) and G alpha(i3) effects on chemokine receptor CXCR3-mediated signaling. Our data showed that G alpha(i2) was indispensable for T cell responses to three CXCR3 ligands, CXCL9, CXCL10, and CXCL11, as the lack of G alpha(i2) abolished CXCR3-stimulated migration and guanosine 5'-3-O-(thio)triphosphate (GTPgammaS) incorporation. In sharp contrast, T cells isolated from G alpha(i3) knock-out mice displayed a significant increase in both GTPgammaS incorporation and migration as compared with wild type T cells when stimulated with CXCR3 agonists. The increased GTPgammaS incorporation was blocked by G alpha(i3) protein in a dose-dependent manner. G alpha(i3)-mediated blockade of G alpha(i2) activation did not result from G alpha(i3) activation, but instead resulted from competition or steric hindrance of G alpha(i2) interaction with the CXCR3 receptor via the N terminus of the second intracellular loop. A mutation in this domain abrogated not only G alpha(i2) activation induced by a CXCR3 agonist but also the interaction of G alpha(i3) to the CXCR3 receptor. These findings reveal for the first time an interplay of G alpha(i) proteins in transmitting G protein-coupled receptor signals. This interplay has heretofore been masked by the use of pertussis toxin, a broad inhibitor of the G alpha(i/o) protein family.
Figures



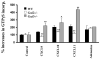
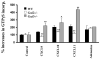
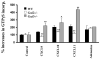
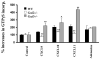


Similar articles
-
The chemokines CXCL9, CXCL10, and CXCL11 differentially stimulate G alpha i-independent signaling and actin responses in human intestinal myofibroblasts.J Immunol. 2005 Oct 15;175(8):5403-11. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.175.8.5403. J Immunol. 2005. PMID: 16210647
-
Pharmacological characterization of CXC chemokine receptor 3 ligands and a small molecule antagonist.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2005 Jun;313(3):1263-71. doi: 10.1124/jpet.105.083683. Epub 2005 Mar 10. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2005. PMID: 15761110
-
CXCR3 internalization following T cell-endothelial cell contact: preferential role of IFN-inducible T cell alpha chemoattractant (CXCL11).J Immunol. 2001 Dec 15;167(12):7084-93. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.167.12.7084. J Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11739530
-
CXCR3 Ligands in Cancer and Autoimmunity, Chemoattraction of Effector T Cells, and Beyond.Front Immunol. 2020 May 29;11:976. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00976. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32547545 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The transmembrane G protein-coupled CXCR3 receptor-ligand system and maternal foetal allograft rejection.Placenta. 2021 Jan 15;104:81-88. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2020.11.003. Epub 2020 Nov 14. Placenta. 2021. PMID: 33296735 Review.
Cited by
-
Variations in Gnai2 and Rgs1 expression affect chemokine receptor signaling and the organization of secondary lymphoid organs.Genes Immun. 2010 Jul;11(5):384-96. doi: 10.1038/gene.2010.27. Epub 2010 May 27. Genes Immun. 2010. PMID: 20508603 Free PMC article.
-
CXCR3 and Cognate Ligands are Associated with Immune Cell Alteration and Aggressiveness of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma.Clin Cancer Res. 2020 Nov 15;26(22):6051-6063. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-1359. Epub 2020 Sep 1. Clin Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32873571 Free PMC article.
-
The CXCL10/CXCR3 Axis and Cardiac Inflammation: Implications for Immunotherapy to Treat Infectious and Noninfectious Diseases of the Heart.J Immunol Res. 2016;2016:4396368. doi: 10.1155/2016/4396368. Epub 2016 Oct 3. J Immunol Res. 2016. PMID: 27795961 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Implications of non-canonical G-protein signaling for the immune system.Cell Signal. 2014 Jun;26(6):1269-82. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.02.010. Epub 2014 Feb 28. Cell Signal. 2014. PMID: 24583286 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A review of the pleiotropic actions of the IFN-inducible CXC chemokine receptor 3 ligands in the synovial microenvironment.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2023 Mar 2;80(3):78. doi: 10.1007/s00018-023-04715-w. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2023. PMID: 36862204 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wilkie TM, Gilbert DJ, Olsen AS, Chen XN, Amatruda TT, Korenberg JR, Trask BJ, de Jong P, Reed RR, Simon MI. Nat.Genet. 1992;1:85–91. - PubMed
-
- Kaslow HR, Burns DL. FASEB J. 1992;6:2684–2690. - PubMed
-
- Kehrl JH. Immunity. 1998;8:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Sunyer T, Monastirsky B, Codina J, Birnbaumer L. Mol.Endocrinol. 1989;3:1115–1124. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

