The small heterodimer partner is a gonadal gatekeeper of sexual maturation in male mice
- PMID: 17289919
- PMCID: PMC1785120
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.409307
The small heterodimer partner is a gonadal gatekeeper of sexual maturation in male mice
Abstract
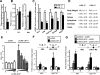
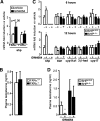
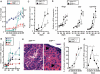
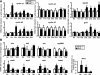
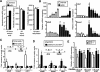
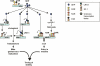
The small heterodimer partner (SHP) is an atypical nuclear receptor known mainly for its role in bile acid homeostasis in the enterohepatic tract. We explore here the role of SHP in the testis. SHP is expressed in the interstitial compartment of the adult testes, which contain the Leydig cells. SHP there inhibits the expression of steroidogenic genes, on the one hand by inhibiting the expression of the nuclear receptors steroidogenic factor-1 and liver receptor homolog-1 (lrh-1), and on the other hand by directly repressing the transcriptional activity of LRH-1. Consequently, in SHP knockout mice, testicular testosterone synthesis is increased independently of the hypothalamus-pituitary axis. Independent of its action on androgen synthesis, SHP also determines the timing of germ cell differentiation by controlling testicular retinoic acid metabolism. Through the inhibition of the transcriptional activity of retinoic acid receptors, SHP controls the expression of stimulated by retinoic acid gene 8 (stra8) - a gene that is indispensable for germ cell meiosis and differentiation. Together, our data demonstrate new roles for SHP in testicular androgen and retinoic acid metabolism, making SHP a testicular gatekeeper of the timing of male sexual maturation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Bile acid-FXRα pathways regulate male sexual maturation in mice.Oncotarget. 2016 Apr 12;7(15):19468-82. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7153. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26848619 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of the link between the hypothalamo-pituitary axis and the testicular orphan nuclear receptor NR0B2 in adult male mice.Endocrinology. 2015 Feb;156(2):660-9. doi: 10.1210/en.2014-1418. Epub 2014 Nov 26. Endocrinology. 2015. PMID: 25426871
-
Distinct roles for steroidogenic factor 1 and desert hedgehog pathways in fetal and adult Leydig cell development.Endocrinology. 2007 Aug;148(8):3704-10. doi: 10.1210/en.2006-1731. Epub 2007 May 10. Endocrinology. 2007. PMID: 17495005
-
Structure and function of the atypical orphan nuclear receptor small heterodimer partner.Int Rev Cytol. 2007;261:117-58. doi: 10.1016/S0074-7696(07)61003-1. Int Rev Cytol. 2007. PMID: 17560281 Review.
-
Retinoic acid, meiosis and germ cell fate in mammals.Development. 2007 Oct;134(19):3401-11. doi: 10.1242/dev.001107. Epub 2007 Aug 22. Development. 2007. PMID: 17715177 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of novel genes and pathways regulated by the orphan nuclear receptor COUP-TFII in mouse MA-10 Leydig cells†.Biol Reprod. 2021 Nov 15;105(5):1283-1306. doi: 10.1093/biolre/ioab131. Biol Reprod. 2021. PMID: 34225363 Free PMC article.
-
Bile acid-FXRα pathways regulate male sexual maturation in mice.Oncotarget. 2016 Apr 12;7(15):19468-82. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7153. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26848619 Free PMC article.
-
The orphan nuclear receptor small heterodimer partner mediates male infertility induced by diethylstilbestrol in mice.J Clin Invest. 2009 Dec;119(12):3752-64. doi: 10.1172/JCI38521. Epub 2009 Nov 2. J Clin Invest. 2009. PMID: 19884658 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription Factors in the Regulation of Leydig Cell Gene Expression and Function.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Apr 7;13:881309. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.881309. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35464056 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Orphan receptor small heterodimer partner suppresses tumorigenesis by modulating cyclin D1 expression and cellular proliferation.Hepatology. 2008 Jul;48(1):289-98. doi: 10.1002/hep.22342. Hepatology. 2008. PMID: 18537191 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abel M.H., Wootton A.N., Wilkins V., Huhtaniemi I., Knight P.G., Charlton H.M., Wootton A.N., Wilkins V., Huhtaniemi I., Knight P.G., Charlton H.M., Wilkins V., Huhtaniemi I., Knight P.G., Charlton H.M., Huhtaniemi I., Knight P.G., Charlton H.M., Knight P.G., Charlton H.M., Charlton H.M. The effect of a null mutation in the follicle-stimulating hormone receptor gene on mouse reproduction. Endocrinology. 2000;141:1795–1803. - PubMed
-
- Argmann C.A., Chambon P., Auwerx J., Chambon P., Auwerx J., Auwerx J. Mouse phenogenomics: The fast track to ‘systems metabolism.’. Cell Metab. 2005;2:349–360. - PubMed
-
- Bakke M., Zhao L., Hanley N.A., Parker K.L., Zhao L., Hanley N.A., Parker K.L., Hanley N.A., Parker K.L., Parker K.L. SF-1: A critical mediator of steroidogenesis. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2001;171:5–7. - PubMed
-
- Baltus A.E., Menke D.B., Hu Y.C., Goodheart M.L., Carpenter A.E., de Rooij D.G., Page D.C., Menke D.B., Hu Y.C., Goodheart M.L., Carpenter A.E., de Rooij D.G., Page D.C., Hu Y.C., Goodheart M.L., Carpenter A.E., de Rooij D.G., Page D.C., Goodheart M.L., Carpenter A.E., de Rooij D.G., Page D.C., Carpenter A.E., de Rooij D.G., Page D.C., de Rooij D.G., Page D.C., Page D.C. In germ cells of mouse embryonic ovaries, the decision to enter meiosis precedes premeiotic DNA replication. Nat. Genet. 2006;38:1430–1434. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Zimra M., Koler M., Orly J., Koler M., Orly J., Orly J. Transcription of cholesterol side-chain cleavage cytochrome P450 in the placenta: Activating protein-2 assumes the role of steroidogenic factor-1 by binding to an overlapping promoter element. Mol. Endocrinol. 2002;16:1864–1880. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
