CD48 is critically involved in allergic eosinophilic airway inflammation
- PMID: 17290046
- PMCID: PMC1899297
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.200605-695OC
CD48 is critically involved in allergic eosinophilic airway inflammation
Abstract
Rationale: Despite ongoing research, the molecular mechanisms controlling asthma are still elusive. CD48 is a glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored protein involved in lymphocyte adhesion, activation, and costimulation. Although CD48 is widely expressed on hematopoietic cells and commonly studied in the context of natural killer and cytotoxic T cell functions, its role in helper T cell type 2 settings has not been examined.
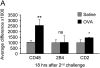
Objectives: To evaluate the expression and function of CD48, CD2, and 2B4 in a murine model of allergic eosinophilic airway inflammation.
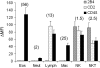
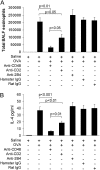
Methods: Allergic eosinophilic airway inflammation was induced by ovalbumin (OVA)-alum sensitization and intranasal inoculation of OVA or, alternatively, by repeated intranasal inoculation of Aspergillus fumigatus antigen in wild-type, STAT (signal transducer and activator of transcription)-6-deficient, and IL-4/IL-13-deficient BALB/c mice. Gene profiling of whole lungs was performed, followed by Northern blot and flow cytometric analysis. Anti-CD48, -CD2, and -2B4 antibodies were administered before OVA challenge and cytokine expression and histology were assessed.
Measurements and main results: Microarray data analysis demonstrated upregulation of CD48 in the lungs of OVA-challenged mice. Allergen-induced CD48 expression was independent of STAT-6, IL-13, and IL-4. Neutralization of CD48 in allergen-challenged mice abrogated bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and lung inflammation. Neutralization of CD2 inhibited the inflammatory response to a lesser extent and neutralization of 2B4 had no effect.
Conclusions: Our results suggest that CD48 is critically involved in allergic eosinophilic airway inflammation. As such, CD48 may provide a new potential target for the suppression of asthma.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Mutational analysis of the human 2B4 (CD244)/CD48 interaction: Lys68 and Glu70 in the V domain of 2B4 are critical for CD48 binding and functional activation of NK cells.J Immunol. 2005 Jul 15;175(2):1005-13. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.175.2.1005. J Immunol. 2005. PMID: 16002700
-
Identification of the 2B4 molecule as a counter-receptor for CD48.J Immunol. 1998 Dec 1;161(11):5809-12. J Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9834056
-
Requirement of homotypic NK-cell interactions through 2B4(CD244)/CD48 in the generation of NK effector functions.Blood. 2006 Apr 15;107(8):3181-8. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-01-0185. Epub 2005 May 19. Blood. 2006. PMID: 15905190 Free PMC article.
-
2B4 (CD244) and CS1: novel members of the CD2 subset of the immunoglobulin superfamily molecules expressed on natural killer cells and other leukocytes.Immunol Rev. 2001 Jun;181:234-49. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-065x.2001.1810120.x. Immunol Rev. 2001. PMID: 11513145 Review.
-
CD48: A co-stimulatory receptor of immunity.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2011 Jan;43(1):25-8. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2010.09.001. Epub 2010 Sep 15. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 20833258 Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-CD48 Monoclonal Antibody Attenuates Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis by Limiting the Number of Pathogenic CD4+ T Cells.J Immunol. 2016 Oct 15;197(8):3038-3048. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1600706. Epub 2016 Aug 31. J Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27581174 Free PMC article.
-
Human mast cell activation by Staphylococcus aureus: interleukin-8 and tumor necrosis factor alpha release and the role of Toll-like receptor 2 and CD48 molecules.Infect Immun. 2008 Oct;76(10):4489-97. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00270-08. Epub 2008 Jul 21. Infect Immun. 2008. PMID: 18644875 Free PMC article.
-
Resistin-like molecule-α regulates IL-13-induced chemokine production but not allergen-induced airway responses.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2012 May;46(5):703-13. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2011-0391OC. Epub 2012 Jan 12. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22246861 Free PMC article.
-
Age-related epigenetic drift deregulates SIRT6 expression and affects its downstream genes in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells.Epigenetics. 2020 Dec;15(12):1336-1347. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2020.1780081. Epub 2020 Jun 23. Epigenetics. 2020. PMID: 32573339 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional Profiling of Mouse Eosinophils Identifies Distinct Gene Signatures Following Cellular Activation.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 14;12:802839. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.802839. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34970274 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Busse WW, Lemanske RF Jr. Asthma. N Engl J Med 2001;344:350–362. - PubMed
-
- Bochner BS, Busse WW. Allergy and asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2005;115:953–959. - PubMed
-
- Busse WW, Rosenwasser LJ. Mechanisms of asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2003;111:S799–S804. - PubMed
-
- Barnes PJ. New drugs for asthma. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2004;3:831–844. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

