Transcription reactivation steps stimulated by oocyte maturation in C. elegans
- PMID: 17291483
- PMCID: PMC1913287
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2006.12.039
Transcription reactivation steps stimulated by oocyte maturation in C. elegans
Abstract
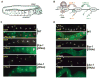
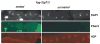
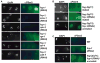
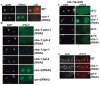
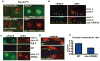
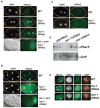
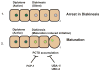
Developing oocytes produce materials that will support early embryonic development then cease transcription before fertilization. Later, a distinct transcription program is established in the embryo. Little is understood about how these global gene regulation transitions are effected. We have investigated in C. elegans how oocyte transcription is influenced by maturation, a process that releases meiotic arrest and prepares for fertilization. By monitoring transcription-associated phosphorylation of the RNA polymerase II (Pol II) C-terminal domain (CTD), we find that oocyte transcription shuts down independently of maturation. Surprisingly, maturation signals then induce CTD phosphorylation that is associated specifically with transcription initiation steps and accumulates to high levels when expression of the CTD phosphatase FCP-1 is inhibited. This CTD phosphorylation is also uncovered when a ubiquitylation pathway is blocked, or when maturation is stimulated precociously. CTD phosphorylation is similarly detected during embryonic mitosis, when transcription is also largely silenced. We conclude that oocyte maturation signals induce abortive transcription events in which FCP-1 may recycle phosphorylated Pol II and that analogous processes may occur during mitosis. Our findings suggest that maturation signals may initiate preparations for embryonic transcription, possibly as part of a broader program that begins the transition from maternal to zygotic gene expression.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Start me up: cell signaling and the journey from oocyte to embryo in C. elegans.Dev Dyn. 2006 Mar;235(3):571-85. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.20662. Dev Dyn. 2006. PMID: 16372336 Review.
-
Expression pattern of HSP25 in mouse preimplantation embryo: heat shock responses during oocyte maturation.Mol Reprod Dev. 2002 Jan;61(1):3-13. doi: 10.1002/mrd.1125. Mol Reprod Dev. 2002. PMID: 11774370
-
Regulated mitochondrial DNA replication during oocyte maturation is essential for successful porcine embryonic development.Biol Reprod. 2007 Feb;76(2):327-35. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.106.054536. Epub 2006 Oct 11. Biol Reprod. 2007. PMID: 17035641
-
Major sperm protein signaling promotes oocyte microtubule reorganization prior to fertilization in Caenorhabditis elegans.Dev Biol. 2006 Nov 1;299(1):105-21. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2006.07.013. Epub 2006 Jul 15. Dev Biol. 2006. PMID: 16919258
-
The Maternal-to-Zygotic Transition in C. elegans.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2015;113:1-42. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctdb.2015.06.001. Epub 2015 Aug 17. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2015. PMID: 26358869 Review.
Cited by
-
New insights into the regulation of RNP granule assembly in oocytes.Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2012;295:233-89. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-394306-4.00013-7. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22449492 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The CERV protein of Cer1, a C. elegans LTR retrotransposon, is required for nuclear export of viral genomic RNA and can form giant nuclear rods.PLoS Genet. 2023 Jun 29;19(6):e1010804. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1010804. eCollection 2023 Jun. PLoS Genet. 2023. PMID: 37384599 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional repression during spermatogenesis in C. elegans requires TOP-2, condensin II, and the MET-2 H3K9 methyltransferase.MicroPubl Biol. 2023 Aug 23;2023:10.17912/micropub.biology.000933. doi: 10.17912/micropub.biology.000933. eCollection 2023. MicroPubl Biol. 2023. PMID: 37692088 Free PMC article.
-
Control of oocyte growth and meiotic maturation in Caenorhabditis elegans.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013;757:277-320. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-4015-4_10. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013. PMID: 22872481 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The TRIM-NHL protein LIN-41 and the OMA RNA-binding proteins antagonistically control the prophase-to-metaphase transition and growth of Caenorhabditis elegans oocytes.Genetics. 2014 Dec;198(4):1535-58. doi: 10.1534/genetics.114.168831. Epub 2014 Sep 26. Genetics. 2014. PMID: 25261698 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baugh LR, Hill AA, Slonim DK, Brown EL, Hunter CP. Composition and dynamics of the Caenorhabditis elegans early embryonic transcriptome. Development. 2003;130:889–900. - PubMed
-
- Bentley DL. Rules of engagement: co-transcriptional recruitment of pre-mRNA processing factors. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2005;17:251–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

