Years of potential life lost among heroin addicts 33 years after treatment
- PMID: 17291577
- PMCID: PMC2039886
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ypmed.2006.10.003
Years of potential life lost among heroin addicts 33 years after treatment
Abstract
Objective: To examine premature mortality in terms of years of potential life lost (YPLL) among a cohort of long-term heroin addicts.
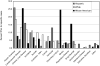
Method: This longitudinal, prospective study followed a cohort of 581 male heroin addicts in California for more than 33 years. In the latest follow-up conducted in 1996/97, 282 subjects (48.5%) were confirmed as deceased by death certificates. YPLL before age 65 years was calculated by causes of death. Ethnic differences in YPLL were assessed among Whites, Hispanics, and African Americans.
Results: On average, addicts in this cohort lost 18.3 years (SD=10.7) of potential life before age 65. Of the total YPLL for the cohort, 22.3% of the years lost was due to heroin overdose, 14.0% due to chronic liver disease, and 10.2% to accidents. The total YPLL and YPLL by death cause in addict cohort were significantly higher than that of US population. The YPLL among African Americans was significantly lower than that among Whites or Hispanics.
Conclusion: The YPLL among addicts was much higher than that in the national population; within the cohort, premature mortality was higher among Whites and Hispanics compared to African American addicts.
Figures
References
-
- Anderson RN, Minino AM, Fingerhut LA, Warner M, Heinen MA. Deaths: injuries, 2001. Natl Vital Stat Rep. 2004;52(21):1–86. - PubMed
-
- Barr HL, Antes D, Ottenberg DJ, Rosen A. Mortality of treated alcoholics and drug addicts: The benefits of abstinence. J Stud Alcohol. 1984;45(5):440–452. - PubMed
-
- Bartu A, Freeman NC, Gawthorne GS, Codde JP, Holman CD. Mortality in a cohort of opiate and amphetamine users in Perth, Western Australia. Addiction. 2004;99(1):53–60. - PubMed
-
- Blumstein A, Rivara FP, Rosenfeld R. The rise and decline of homicide--and why. Annu Rev Public Health. 2000;21:505–41. Review. - PubMed
-
- Booth MW, Castro RG, Anglin MD. What do we know about Hispanic substance abuse? A review of the literature. In: Glick R, Moore J, editors. Drugs in Hispanic Communities. Rutgers University Press; New Brunswick, NJ: 1991. pp. 21–43.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical