Ultrasonically targeted delivery into endothelial and smooth muscle cells in ex vivo arteries
- PMID: 17291619
- PMCID: PMC1892790
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2006.12.029
Ultrasonically targeted delivery into endothelial and smooth muscle cells in ex vivo arteries
Abstract
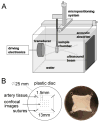
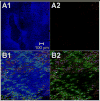
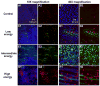
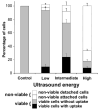
This study tested the hypothesis that ultrasound can target intracellular uptake of drugs into vascular endothelial cells (ECs) at low to intermediate energy and into smooth muscle cells (SMCs) at high energy. Ultrasound-enhanced delivery has been shown to enhance and target intracellular drug and gene delivery in the vasculature to treat cardiovascular disease, but quantitative studies of the delivery process are lacking. Viable ex vivo porcine carotid arteries were placed in a solution containing a model drug, TO-PRO(R)-1, and Optison microbubbles. Arteries were exposed to ultrasound at 1.1 MHz and acoustic energies of 5.0, 66, or 630 J/cm(2). Using confocal microscopy and fluorescent labeling of cells, the artery endothelium and media were imaged to determine the localization and to quantify intracellular uptake and cell death. At low to intermediate ultrasound energy, ultrasound was shown to target intracellular delivery into viable cells that represented 9-24% of exposed ECs. These conditions also typically caused 7-25% EC death. At high energy, intracellular delivery was targeted to SMCs, which was associated with denuding or death of proximal ECs. This work represents the first known in-depth study to evaluate intracellular uptake into cells in tissue. We conclude that significant intracellular uptake of molecules can be targeted into ECs and SMCs by ultrasound-enhanced delivery suggesting possible applications for treatment of cardiovascular diseases and dysfunctions.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Clusters of proliferating endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells in rabbit carotid arteries.Pathol Int. 2015 Nov;65(11):585-94. doi: 10.1111/pin.12348. Epub 2015 Sep 7. Pathol Int. 2015. PMID: 26345370
-
Ultrasound-mediated delivery of echogenic immunoliposomes to porcine vascular smooth muscle cells in vivo.J Liposome Res. 2010 Jun;20(2):160-7. doi: 10.3109/08982100903218918. J Liposome Res. 2010. PMID: 19842795 Free PMC article.
-
Cytotoxic effects of polyhexanide on cellular repopulation and calcification of decellularized equine carotids in vitro and in vivo.Int J Artif Organs. 2013 Mar;36(3):184-94. doi: 10.5301/IJAO.5000182. Epub 2013 Feb 13. Int J Artif Organs. 2013. PMID: 23404640
-
Smooth muscle apoptosis and vascular remodeling.Curr Opin Hematol. 2008 May;15(3):250-4. doi: 10.1097/MOH.0b013e3282f97d71. Curr Opin Hematol. 2008. PMID: 18391793 Review.
-
Transient receptor potential channels and vascular function.Clin Sci (Lond). 2010 Apr 7;119(1):19-36. doi: 10.1042/CS20090641. Clin Sci (Lond). 2010. PMID: 20370719 Review.
Cited by
-
Real-time assessment of ultrasound-mediated drug delivery using fibered confocal fluorescence microscopy.Mol Imaging Biol. 2013 Feb;15(1):3-11. doi: 10.1007/s11307-012-0568-9. Mol Imaging Biol. 2013. PMID: 22707046
-
Microfabricated implants for applications in therapeutic delivery, tissue engineering, and biosensing.Lab Chip. 2008 Nov;8(11):1864-78. doi: 10.1039/b806446f. Epub 2008 Sep 19. Lab Chip. 2008. PMID: 18941687 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Photo-Mediated Ultrasound Therapy on Nitric Oxide and Prostacyclin from Endothelial Cells.Appl Sci (Basel). 2022 Mar 1;12(5):2617. doi: 10.3390/app12052617. Epub 2022 Mar 3. Appl Sci (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35983461 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound-Targeted Microbubble Destruction: Modulation in the Tumor Microenvironment and Application in Tumor Immunotherapy.Front Immunol. 2022 Jul 1;13:937344. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.937344. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35844515 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Can ultrasound enable efficient intracellular uptake of molecules? A retrospective literature review and analysis.Ultrasound Med Biol. 2012 May;38(5):876-88. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2012.01.006. Epub 2012 Mar 16. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2012. PMID: 22425381 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Smith SC, Jr, Jackson R, Pearson TA, Fuster V, Yusuf S, Faergeman O, Wood DA, Alderman M, Horgan J, Home P, Hunn M, Grundy SM. Principles for national and regional guidelines on cardiovascular disease prevention: a scientific statement from the World Heart and Stroke Forum. Circulation. 2004;109(25):3112–3121. - PubMed
-
- Cooke JP. The endothelium: a new target for therapy. Vasc Med. 2000;5(1):49–53. - PubMed
-
- Melo LG, Gnecchi M, Pachori AS, Kong D, Wang K, Liu X, Pratt RE, Dzau VJ. Endothelium-targeted gene and cell-based therapies for cardiovascular disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2004;24(10):1761–1774. - PubMed
-
- Cines DB, Pollak ES, Buck CA, Loscalzo J, Zimmerman GA, McEver RP, Pober JS, Wick TM, Konkle BA, Schwartz BS, Barnathan ES, McCrae KR, Hug BA, Schmidt AM, Stern DM. Endothelial cells in physiology and in the pathophysiology of vascular disorders. Blood. 1998;91(10):3527–3561. - PubMed
-
- Tozer GM, Kanthou C, Baguley BC. Disrupting tumour blood vessels. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5(6):423–435. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

