Effects of NGF and BDNF on baseline glutamate and dopamine release in the hippocampal formation of the adult rat
- PMID: 17292337
- PMCID: PMC2692481
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2007.01.018
Effects of NGF and BDNF on baseline glutamate and dopamine release in the hippocampal formation of the adult rat
Abstract
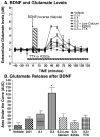
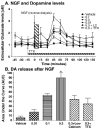
It has been shown using in vitro techniques that BDNF and NGF evoke neurotransmitter release in the hippocampus but this phenomenon has not been demonstrated in vivo to date. We therefore performed in vivo microdialysis in urethane-anesthetized Fischer 344 rats. The microdialysis probe was implanted stereotaxically into the CA1 area of the hippocampus. Three hours after the implantation of the probe, glutamate (Glu) and dopamine (DA) levels had reached a stable baseline. Four baseline samples were collected every 15 min at a flow rate of 1 microL/min. The growth factors were delivered (1 microL/10 min) using a microinjector attached to the microdialysis probe. We found that BDNF and NGF, when administered into the hippocampus, evoked dopamine and glutamate release in a dose-dependent fashion. NGF produced a biphasic response in the release of Glu, and a uniphasic response in the release of DA, both of which were calcium dependent. The neurotransmitter release induced by NGF was blocked by tetrodotoxin, indicating neuronal origin of this response. The BDNF induced release of DA and Glu was decreased in low calcium conditions, indicating that it is at least partially calcium dependent. Furthermore, BDNF-induced neurotransmitter release was partially blocked by pre-treatment with K252a, an antagonist for tyrosine kinase receptors, indicating that BDNF is acting through Trk receptors to induce neurotransmitter release. These results demonstrate a close relationship between the growth factors BDNF and NGF and the neurotransmitters DA and Glu in the hippocampus of intact animals.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor facilitates glutamate and inhibits GABA release from hippocampal synaptosomes through different mechanisms.Brain Res. 2004 Jul 30;1016(1):72-8. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2004.04.070. Brain Res. 2004. PMID: 15234254
-
Nerve growth factor and brain-derived neurotrophic factor increase neurotransmitter release in the rat visual cortex.Eur J Neurosci. 1998 Jun;10(6):2185-91. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9568.1998.00227.x. Eur J Neurosci. 1998. PMID: 9753104
-
Rapid stimulatory effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin-3 on somatostatin release and intracellular calcium rise in primary hypothalamic cell cultures.Neuroendocrinology. 2001 Jul;74(1):43-54. doi: 10.1159/000054669. Neuroendocrinology. 2001. PMID: 11435757
-
Modulation of neurotransmitter release induced by brain-derived neurotrophic factor in rat brain striatal slices in vitro.Brain Res. 2002 Jun 21;941(1-2):34-42. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(02)02505-2. Brain Res. 2002. PMID: 12031545
-
Functional interactions between somatodendritic dopamine release, glutamate receptors and brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression in mesencephalic structures of the brain.Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2004 Dec;47(1-3):126-44. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresrev.2004.05.002. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2004. PMID: 15572168 Review.
Cited by
-
Short-chain fatty acids promote the effect of environmental signals on the gut microbiome and metabolome in mice.Commun Biol. 2022 May 31;5(1):517. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-03468-9. Commun Biol. 2022. PMID: 35641653 Free PMC article.
-
BDNF Therapeutic Mechanisms in Neuropsychiatric Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 29;23(15):8417. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158417. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35955546 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor, and Plasma Catecholamine Metabolites in People with Major Depression: Preliminary Cross-Sectional Study.Front Psychiatry. 2018 Feb 28;9:52. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00052. eCollection 2018. Front Psychiatry. 2018. PMID: 29541037 Free PMC article.
-
The TrkB-positive dopaminergic neurons are less sensitive to MPTP insult in the substantia nigra of adult C57/BL mice.Neurochem Res. 2011 Oct;36(10):1759-66. doi: 10.1007/s11064-011-0491-5. Epub 2011 May 12. Neurochem Res. 2011. PMID: 21562748
-
Serum Renalase Levels Are Predicted by Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and Associated with Cardiovascular Events and Mortality after Percutaneous Coronary Intervention.J Clin Med. 2018 Nov 12;7(11):437. doi: 10.3390/jcm7110437. J Clin Med. 2018. PMID: 30424498 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albeck DS, Backman C, Veng L, Friden P, Rose GM, Granholm A. Acute application of NGF increases the firing rate of aged rat basal forebrain neurons. Eur J Neurosci. 1999;11:2291–2304. - PubMed
-
- Amino S, Itakura M, Ohnishi H, Tsujimura J, Koizumi S, Takei N, Takahashi M. J Biochem (Tokyo) Vol. 131. 2002. Nerve growth factor enhances neurotransmitter release from PC12 cells by increasing Ca(2+)-responsible secretory vesicles through the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; pp. 887–894. - PubMed
-
- Bimonte HA, Nelson ME, Granholm AC. Age-related deficits as working memory load increases: relationships with growth factors. Neurobiol Aging. 2003;24:37–48. - PubMed
-
- Blochl A, Sirrenberg C. Neurotrophins stimulate the release of dopamine from rat mesencephalic neurons via Trk and p75Lntr receptors. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:21100–21107. - PubMed
-
- Bramham CR, Southard T, Sarvey JM, Herkenham M, Brady LS. Unilateral LTP triggers bilateral increases in hippocampal neurotrophin and Trk receptor mRNA expression in behaving rats: evidence for interhemispheric communication. J Comp Neurol. 1996;368:371–382. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

