Signaling pathways involved in OxPAPC-induced pulmonary endothelial barrier protection
- PMID: 17292425
- PMCID: PMC1934559
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mvr.2006.12.004
Signaling pathways involved in OxPAPC-induced pulmonary endothelial barrier protection
Abstract
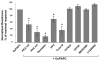
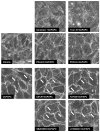
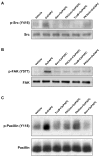
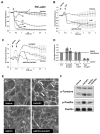
Increased tissue or serum levels of oxidized phospholipids have been detected in a variety of chronic and acute pathological conditions such as hyperlipidemia, atherosclerosis, heart attack, cell apoptosis, acute inflammation and injury. We have recently described signaling cascades activated by oxidized 1-palmitoyl-2-arachidonoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (OxPAPC)in the human pulmonary artery endothelial cells (EC) and reported potent barrier-protective effects of OxPAPC, which were mediated by small GTPases Rac and Cdc42. In this study we have further characterized signal transduction pathways involved in the OxPAPC-mediated endothelial barrier protection. Inhibitors of small GTPases, protein kinase A (PKA), protein kinase C (PKC), Src family kinases and general inhibitors of tyrosine kinases attenuated OxPAPC-induced barrier-protective response and EC cytoskeletal remodeling. In contrast, small GTPase Rho, Rho kinase, Erk-1,2 MAP kinase and p38 MAP kinase and PI3-kinase were not involved in the barrier-protective effects of OxPAPC. Inhibitors of PKA, PKC, tyrosine kinases and small GTPase inhibitor toxin B suppressed OxPAPC-induced Rac activation and decreased phosphorylation of focal adhesion kinase (FAK) and paxillin. Barrier-protective effects of OxPAPC were not reproduced by platelet activating factor (PAF), which at high concentrations induced barrier dysfunction, but were partially attenuated by PAF receptor antagonist A85783. These results demonstrate for the first time upstream signaling cascades involved in the OxPAPC-induced Rac activation, cytoskeletal remodeling and barrier regulation and suggest PAF receptor-independent mechanisms of OxPAPC-mediated endothelial barrier protection.
Figures

References
-
- Birukov KG. Oxidized lipids: the two faces of vascular inflammation. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2006;8(3):223–31. - PubMed
-
- Birukov KG, Birukova AA, et al. Shear stress-mediated cytoskeletal remodeling and cortactin translocation in pulmonary endothelial cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2002;26(4):453–64. - PubMed
-
- Birukov KG, V, Bochkov N, et al. Epoxycyclopentenone-containing oxidized phospholipids restore endothelial barrier function via Cdc42 and Rac. Circ Res. 2004;95(9):892–901. - PubMed
-
- Birukov KG, Leitinger N, et al. Signal transduction pathways activated in human pulmonary endothelial cells by OxPAPC, a bioactive component of oxidized lipoproteins. Microvasc Res. 2004;67(1):18–28. - PubMed
-
- Birukova AA, Adyshev D, et al. ALK5 and Smad4 are involved in TGF-beta1-induced pulmonary endothelial permeability. FEBS Lett. 2005;579(18):4031–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

