Phylogenetic appearance of neuropeptide S precursor proteins in tetrapods
- PMID: 17293003
- PMCID: PMC1868679
- DOI: 10.1016/j.peptides.2007.01.008
Phylogenetic appearance of neuropeptide S precursor proteins in tetrapods
Abstract
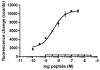
Sleep and emotional behavior are two hallmarks of vertebrate animal behavior, implying that specialized neuronal circuits and dedicated neurochemical messengers may have been developed during evolution to regulate such complex behaviors. Neuropeptide S (NPS) is a newly identified peptide transmitter that activates a typical G protein-coupled receptor. Central administration of NPS produces profound arousal, enhances wakefulness and suppresses all stages of sleep. In addition, NPS can alleviate behavioral responses to stress by producing anxiolytic-like effects. A bioinformatic analysis of current genome databases revealed that the NPS peptide precursor gene is present in all vertebrates with the exception of fish. A high level of sequence conservation, especially of aminoterminal structures was detected, indicating stringent requirements for agonist-induced receptor activation. Duplication of the NPS precursor gene was only found in one out of two marsupial species with sufficient genome coverage (Monodelphis domestica; opossum), indicating that the duplicated opossum NPS sequence might have arisen as an isolated event. Pharmacological analysis of both Monodelphis NPS peptides revealed that only the closely related NPS peptide retained agonistic activity at NPS receptors. The duplicated precursor might be either a pseudogene or could have evolved different receptor selectivity. Together, these data show that NPS is a relatively recent gene in vertebrate evolution whose appearance might coincide with its specialized physiological functions in terrestrial vertebrates.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Discovery of sea urchin NGFFFamide receptor unites a bilaterian neuropeptide family.Open Biol. 2015 Apr;5(4):150030. doi: 10.1098/rsob.150030. Open Biol. 2015. PMID: 25904544 Free PMC article.
-
Neuropeptide S as a novel arousal promoting peptide transmitter.FEBS J. 2005 Nov;272(22):5689-93. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2005.04982.x. FEBS J. 2005. PMID: 16279934 Review.
-
Neuropeptide S: a neuropeptide promoting arousal and anxiolytic-like effects.Neuron. 2004 Aug 19;43(4):487-97. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2004.08.005. Neuron. 2004. PMID: 15312648
-
Cloning and distribution of neuropeptide S and its receptor in the pig.Neuropeptides. 2009 Dec;43(6):465-81. doi: 10.1016/j.npep.2009.09.003. Epub 2009 Oct 24. Neuropeptides. 2009. PMID: 19854507
-
Neuropeptide S: a new player in the modulation of arousal and anxiety.Mol Interv. 2005 Feb;5(1):42-6. doi: 10.1124/mi5.1.8. Mol Interv. 2005. PMID: 15731503 Review.
Cited by
-
Importance of extracellular loop one of the neuropeptide S receptor for biogenesis and function.Peptides. 2010 Jan;31(1):130-8. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2009.10.015. Epub 2009 Oct 27. Peptides. 2010. PMID: 19874863 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacology of neuropeptide S in mice: therapeutic relevance to anxiety disorders.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2008 May;197(4):601-11. doi: 10.1007/s00213-008-1080-4. Epub 2008 Mar 3. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2008. PMID: 18311561
-
Pharmacology, Physiology and Genetics of the Neuropeptide S System.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021 Apr 23;14(5):401. doi: 10.3390/ph14050401. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33922620 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Discovery of sea urchin NGFFFamide receptor unites a bilaterian neuropeptide family.Open Biol. 2015 Apr;5(4):150030. doi: 10.1098/rsob.150030. Open Biol. 2015. PMID: 25904544 Free PMC article.
-
Human Neuropeptide S Receptor Is Activated via a Gαq Protein-biased Signaling Cascade by a Human Neuropeptide S Analog Lacking the C-terminal 10 Residues.J Biol Chem. 2016 Apr 1;291(14):7505-16. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.704122. Epub 2016 Feb 10. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26865629 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alvarez CE, Sutcliffe JG. Hypocretin is an early member of the incretin gene family. Neurosci Lett. 2002;324:169–72. - PubMed
-
- Bernier V, Stocco R, Bogusky MJ, Joyce JG, Parachoniak C, Grenier K, Arget M, Mathieu MC, O’Neill GP, Slipetz D, Crackower MA, Tan CM, Therien AG. Structure-function relationships in the neuropeptide S receptor: molecular consequences of the asthma-associated mutation N107I. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:24704–12. - PubMed
-
- Chartrel N, Bruzzone F, Leprince J, Tollemer H, Anouar Y, Do-Rego JC, Segalas-Milazzo I, Guilhaudis L, Cosette P, Jouenne T, Simonnet G, Vallarino M, Beauvillain JC, Costentin J, Vaudry H. Structure and functions of the novel hypothalamic RFamide neuropeptides R-RFa and 26RFa in vertebrates. Peptides. 2006;27:1110–20. - PubMed
-
- Conlon JM. The origin and evolution of peptide YY (PYY) and pancreatic polypeptide (PP) Peptides. 2002;23:269–78. - PubMed
-
- Danielson PB, Dores RM. Molecular evolution of the opioid/orphanin gene family. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1999;113:169–86. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

