Peptide stabilized amphotericin B nanodisks
- PMID: 17293004
- PMCID: PMC1863120
- DOI: 10.1016/j.peptides.2007.01.007
Peptide stabilized amphotericin B nanodisks
Abstract
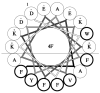
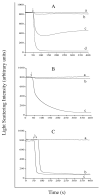
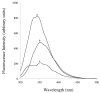
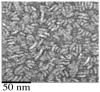
Nanometer scale apolipoprotein A-I stabilized phospholipid disk complexes (nanodisks; ND) have been formulated with the polyene antibiotic amphotericin B (AMB). The present studies were designed to evaluate if a peptide can substitute for the function of the apolipoprotein component of ND with respect to particle formation and stability. An 18-residue synthetic amphipathic alpha-helical peptide, termed 4F (Ac-D-W-F-K-A-F-Y-D-K-V-A-E-K-F-K-E-A-F-NH(2)), solubilized vesicles comprised of egg phosphatidylcholine (egg PC), dipentadecanoyl PC or dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine (DMPC) at rates greater than or equal to solubilization rates observed with human apolipoprotein A-I (apoA-I; 243 amino acids). Characterization studies revealed that interaction with DMPC induced a near doubling of 4F tryptophan fluorescence emission quantum yield (excitation 280 nm) and a approximately 7 nm blue shift in emission wavelength maximum. Inclusion of AMB in the vesicle substrate resulted in formation of 4F AMB-ND. Spectra of AMB containing particles revealed the antibiotic is a highly effective quencher of 4F tryptophan fluorescence emission, giving rise to a Ksv=7.7 x 10(4). Negative stain electron microscopy revealed that AMB-ND prepared with 4F possessed a disk shaped morphology similar to ND prepared without AMB or prepared with apoA-I. In yeast and pathogenic fungi growth inhibition assays, 4F AMB-ND was as effective as apoA-I AMB-ND. The data indicate that AMB-ND generated using an amphipathic peptide in lieu of apoA-I form a discrete population of particles that possess potent biological activity. Given their intrinsic versatility, peptides may be preferred for scale up and clinical application of AMB-ND.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nanodisks derived from amphotericin B lipid complex.J Pharm Sci. 2008 Oct;97(10):4425-32. doi: 10.1002/jps.21325. J Pharm Sci. 2008. PMID: 18271034 Free PMC article.
-
Reconstituted high density lipoprotein enriched with the polyene antibiotic amphotericin B.J Lipid Res. 2006 Feb;47(2):260-7. doi: 10.1194/jlr.D500033-JLR200. Epub 2005 Nov 28. J Lipid Res. 2006. PMID: 16314670
-
Spectroscopic studies of amphotericin B solubilized in nanoscale bilayer membranes.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006 Jan;1758(1):38-44. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2006.01.001. Epub 2006 Jan 26. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006. PMID: 16473324
-
Molecular modelling of membrane activity of amphotericin B, a polyene macrolide antifungal antibiotic.Acta Biochim Pol. 2005;52(3):655-8. Epub 2005 Aug 5. Acta Biochim Pol. 2005. PMID: 16086075 Review.
-
The Role of Signaling via Aqueous Pore Formation in Resistance Responses to Amphotericin B.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016 Aug 22;60(9):5122-9. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00878-16. Print 2016 Sep. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016. PMID: 27381391 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Spontaneous Lipid Nanodisc Fomation by Amphiphilic Polymethacrylate Copolymers.J Am Chem Soc. 2017 Dec 27;139(51):18657-18663. doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b10591. Epub 2017 Dec 5. J Am Chem Soc. 2017. PMID: 29171274 Free PMC article.
-
Nanodisks derived from amphotericin B lipid complex.J Pharm Sci. 2008 Oct;97(10):4425-32. doi: 10.1002/jps.21325. J Pharm Sci. 2008. PMID: 18271034 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt3a nanodisks promote ex vivo expansion of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells.J Nanobiotechnology. 2016 Aug 23;14(1):66. doi: 10.1186/s12951-016-0218-5. J Nanobiotechnology. 2016. PMID: 27553039 Free PMC article.
-
All-trans-retinoic acid nanodisks.Int J Pharm. 2007 Jul 18;339(1-2):246-50. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2007.02.033. Epub 2007 Mar 6. Int J Pharm. 2007. PMID: 17412536 Free PMC article.
-
Nanolipoprotein particles for co-delivery of cystine-knot peptides and Fab-based therapeutics.Nanoscale Adv. 2021 Jun 1;3(13):3929-3941. doi: 10.1039/d1na00218j. eCollection 2021 Jun 30. Nanoscale Adv. 2021. PMID: 36133017 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bolard J, Legrand P, Heitz F, Cybulska B. One-sided action of amphotericin B on cholesterol-containing membranes is determined by its self-association in the medium. Biochemistry. 1991;30:5707–15. - PubMed
-
- Datta G, Chaddha M, Hama S, Navab M, Fogelman AM, Garber DW, et al. Effects of increasing hydrophobicity on the physical-chemical and biological properties of a class A amphipathic helical peptide. J Lipid Res. 2001;42:1096–104. - PubMed
-
- Davidson WS, Silva RA. Apolipoprotein structural organization in high density lipoproteins: belts, bundles, hinges and hairpins. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2005;16:295–300. - PubMed
-
- Hristova K, Wimley WC, Mishra VK, Anantharamiah GM, Segrest JP, White SH. An amphipathic alpha-helix at a membrane interface: a structural study using a novel X-ray diffraction method. J Mol Biol. 1999;290:99–117. - PubMed
-
- Mishra VK, Anantharamaiah GM, Segrest JP, Palgunachari MN, Chaddha M, Sham SW, et al. Association of a model class A (apolipoprotein) amphipathic alpha helical peptide with lipid: high resolution NMR studies of peptide.lipid discoidal complexes. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:6511–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

