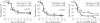Limited efficacy of conventional DMARDs after initial methotrexate failure in patients with recent onset rheumatoid arthritis treated according to the disease activity score
- PMID: 17293364
- PMCID: PMC1994290
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.2006.066662
Limited efficacy of conventional DMARDs after initial methotrexate failure in patients with recent onset rheumatoid arthritis treated according to the disease activity score
Abstract
Objectives: To determine the efficacy of subsequent disease modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD) therapies after initial methotrexate (MTX) failure in patients with recent onset rheumatoid arthritis (RA), treated according to the DAS for 2 years.
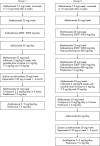
Methods: In groups 1 and 2 of the BeSt study, 244 RA patients were initially treated with MTX 15-25 mg/week. Patients who discontinued MTX because of insufficient clinical response (disease activity score, DAS >2.4) or toxicity were classified as "MTX failures." In group 1, these patients switched to sulfasalazine (SSA), then leflunomide and finally to MTX + infliximab (IFX). In group 2, "MTX failures" added SSA to MTX, then hydroxychloroquine (HCQ), then prednisone, and eventually switched to MTX + IFX. "MTX successes" were patients who achieved a DAS </=2.4 after 2 years while still on MTX monotherapy. Total Sharp/van der Heijde score (TSS) progression from 0-2 years was assessed in "MTX failures" versus "MTX successes."
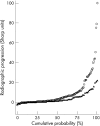
Results: After 2 years, 162/244 patients (66%) had discontinued MTX because of insufficient response or toxicity. Of these, 78% also failed on SSA (adding or switching), 87% subsequently failed on leflunomide (in group 1), and 64% on MTX + SSA + HCQ (in group 2). 34 of 48 patients (71%) in groups 1 and 2 were successfully treated with MTX + IFX. After 2 years, regardless of the "success" on subsequent DMARDs, " MTX failures" had a median TSS progression of 3 units (mean 9) versus 1 unit (mean 3) in "MTX successes" (p = 0.007).
Conclusion: After failure on initial MTX, treatment with subsequent conventional DMARDs is unlikely to result in a DAS </=2.4 and allows progression of joint damage.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: Professor Dr FC Breedveld did a paid expert testimony for Centocor in 1996 and was a paid speaker in a Schering Plough sponsored symposia. Dr CF Allaart was a paid speaker in a Schering Plough sponsored symposium in 2006.
Comment in
-
What is the optimal treatment for patients with RA who fail to respond to monotherapy with methotrexate?Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2008 Jul;4(7):346-7. doi: 10.1038/ncprheum0830. Epub 2008 Jun 10. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2008. PMID: 18542107 No abstract available.
References
-
- Scott D L, Symmons D P, Coulton B L, Popert A J. Long‐term outcome of treating rheumatoid arthritis: results after 20 years. Lancet 19873291108–1111. - PubMed
-
- Smolen J S, Kalden J R, Scott D L, Rozman B, Kvien T K, Larsen A.et al Efficacy and safety of leflunomide compared with placebo and sulphasalazine in active rheumatoid arthritis: a double‐blind, randomised, multicentre trial. European Leflunomide Study Group. Lancet 1999353259–266. - PubMed
-
- Strand V, Cohen S, Schiff M, Weaver A, Fleischmann R, Cannon G.et al Treatment of active rheumatoid arthritis with leflunomide compared with placebo and methotrexate. Leflunomide Rheumatoid Arthritis Investigators Group. Arch Intern Med 19991592542–2550. - PubMed
-
- Aletaha D, Smolen J S. The rheumatoid arthritis patient in the clinic: comparing more than 1,300 consecutive DMARD courses. Rheumatology 2002411367–1374. - PubMed
-
- Pincus T, Yazici Y, Sokka T, Aletaha D, Smolen J S. Methotrexate as the “anchor drug” for the treatment of early rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 200321(Suppl 31)S179–S185. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials