In vitro analysis of the two-component system MtrB-MtrA from Corynebacterium glutamicum
- PMID: 17293417
- PMCID: PMC1855877
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01920-06
In vitro analysis of the two-component system MtrB-MtrA from Corynebacterium glutamicum
Abstract
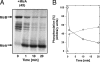
The two-component system MtrBA is involved in the osmostress response of Corynebacterium glutamicum. MtrB was reconstituted in a functionally active form in liposomes and showed autophosphorylation and phosphatase activity. In proteoliposomes, MtrB activity was stimulated by monovalent cations used by many osmosensors for the detection of hypertonicity. Although MtrB was activated by monovalent cations, they lead in vitro to a general stabilization of histidine kinases and do not represent the stimulus for MtrB to sense hyperosmotic stress.
Figures

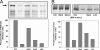
Similar articles
-
Two-component signal transduction in Corynebacterium glutamicum and other corynebacteria: on the way towards stimuli and targets.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2012 Jun;94(5):1131-50. doi: 10.1007/s00253-012-4060-x. Epub 2012 Apr 28. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 22539022 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Osmosensing and osmosignaling in Corynebacterium glutamicum.Amino Acids. 2009 Sep;37(3):487-97. doi: 10.1007/s00726-009-0271-6. Epub 2009 Mar 24. Amino Acids. 2009. PMID: 19308662 Review.
-
Osmosensing properties of the histidine protein kinase MtrB from Corynebacterium glutamicum.J Biol Chem. 2007 Sep 21;282(38):27666-77. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M701749200. Epub 2007 Jul 23. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17650500
-
Deletion of the genes encoding the MtrA-MtrB two-component system of Corynebacterium glutamicum has a strong influence on cell morphology, antibiotics susceptibility and expression of genes involved in osmoprotection.Mol Microbiol. 2004 Oct;54(2):420-38. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2004.04249.x. Mol Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15469514
-
Two-component kinase TrcS complements Mycobacterium smegmatis mtrB kinase mutant.Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2019 May;116S:S107-S113. doi: 10.1016/j.tube.2019.04.017. Epub 2019 May 3. Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2019. PMID: 31088763
Cited by
-
Transcriptome profiles of high-lysine adaptation reveal insights into osmotic stress response in Corynebacterium glutamicum.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Aug 9;10:933325. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.933325. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 36017356 Free PMC article.
-
Two-component signal transduction in Corynebacterium glutamicum and other corynebacteria: on the way towards stimuli and targets.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2012 Jun;94(5):1131-50. doi: 10.1007/s00253-012-4060-x. Epub 2012 Apr 28. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 22539022 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Subcellular localization and characterization of the ParAB system from Corynebacterium glutamicum.J Bacteriol. 2010 Jul;192(13):3441-51. doi: 10.1128/JB.00214-10. Epub 2010 Apr 30. J Bacteriol. 2010. PMID: 20435732 Free PMC article.
-
Biomimetic Materials to Fabricate Artificial Cells.Chem Rev. 2024 Dec 11;124(23):13178-13215. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.4c00241. Epub 2024 Nov 26. Chem Rev. 2024. PMID: 39591535 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemical Neural Networks Inside Synthetic Cells? A Proposal for Their Realization and Modeling.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Jun 6;10:927110. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.927110. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35733531 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Ausubel, F. M., R. Brent, R. E. Kingston, D. D. Moore, J. G. Seidman, J. A. Smith, and K. Struhl (ed.). 2002. Short protocols in molecular biology. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, Germany.
-
- Brocker, M., and M. Bott. 2006. Evidence for activator and repressor functions of the response regulator MtrA from Corynebacterium glutamicum. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 264:205-512. - PubMed
-
- Culham, D. E., J. Henderson, R. A. Crane, and J. M. Wood. 2003. Osmosensor ProP of Escherichia coli responds to concentration, chemistry, and molecular size of osmolytes in the proteoliposome lumen. Biochemistry 42:410-420. - PubMed
-
- Dinnbier, U., E. Limpinsel, R. Schmid, and E. P. Bakker. 1988. Transient accumulation of potassium glutamate and its replacement by trehalose during adaptation of growing cells of Escherichia coli K-12 to elevated sodium chloride concentrations. Arch. Microbiol. 150:348-357. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

