Hyaluronan and CD44 antagonize mitogen-dependent cyclin D1 expression in mesenchymal cells
- PMID: 17296798
- PMCID: PMC2063987
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200611058
Hyaluronan and CD44 antagonize mitogen-dependent cyclin D1 expression in mesenchymal cells
Abstract
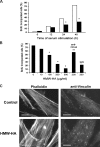
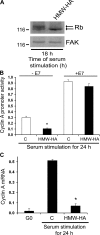
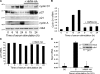
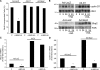
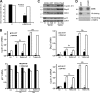
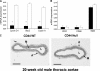
High molecular weight (HMW) hyaluronan (HA) is widely distributed in the extracellular matrix, but its biological activities remain incompletely understood. We previously reported that HMW-HA binding to CD44 antagonizes mitogen-induced S-phase entry in vascular smooth muscle cells (SMCs; Cuff, C.A., D. Kothapalli, I. Azonobi, S. Chun, Y. Zhang, R. Belkin, C. Yeh, A. Secreto, R.K. Assoian, D.J. Rader, and E. Puré. 2001. J. Clin. Invest. 108:1031-1040); we now characterize the underlying molecular mechanism and document its relevance in vivo. HMW-HA inhibits the mitogen-dependent induction of cyclin D1 and down-regulation of p27(kip1) in vascular SMCs. p27(kip1) messenger RNA levels were unaffected by HMW-HA, but the expression of Skp2, the rate-limiting component of the SCF complex that degrades p27(kip1), was reduced. Rescue experiments identified cyclin D1 as the primary target of HMW-HA. Similar results were observed in fibroblasts, and these antimitogenic effects were not detected in CD44-null cells. Analysis of arteries from wild-type and CD44-null mice showed that the effects of HMW-HA/CD44 on cyclin D1 and Skp2 gene expression are detected in vivo and are associated with altered SMC proliferation after vascular injury.
Figures

References
-
- Aruffo, A., I. Stamenkovic, M. Melnick, C.B. Underhill, and B. Seed. 1990. CD44 is the principal cell surface receptor for hyaluronate. Cell. 61:1303–1313. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

