Comparison of the temporary diagnostic relief of transforaminal epidural steroid injection approaches: conventional versus posterolateral technique
- PMID: 17296980
- PMCID: PMC7977402
Comparison of the temporary diagnostic relief of transforaminal epidural steroid injection approaches: conventional versus posterolateral technique
Abstract
Background and purpose: Conventional transforaminal epidural steroid injection (TFESI) has several problems. The purpose of this study was to compare the temporary diagnostic relief and advantages of TFESI performed using the conventional and posterolateral approaches.
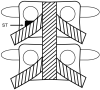
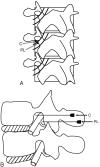
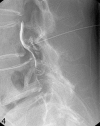
Methods: From August to December 2004, 187 patients received TFESI for lumbar radicular pain. A total of 108 patients (65 women, 43 men; mean age, 56 years) fulfilled the inclusion criteria. In essence, the needle target point was the "safe triangle," but if there was a possibility that the needle could penetrate the nerve root or that the injectate could contact spinal nerve, posterolateral TFESI was used as an alternative. Image analyses of needle positions and chart reviews were performed. Logistic regression analysis and t test were used for statistical analysis.
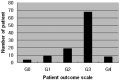
Results: Of the 108 patients, 75 (69.4%) showed an improvement at 2 weeks after TFESI. In 46 patients (42.6%), the needle was located in the posterolateral epidural space, and 33 (71.7%) of those experienced pain relief. Of the 62 patients in whom the needle was located in the anterior epidural position, 42 (68%) experienced pain relief. There was a significant reduction in pain sense for the posterolateral approach (P < .05). However, no statistical difference was found between the 2 approaches and temporary diagnostic relief, and no correlation was found between the other variables tested and temporary diagnostic relief (P > .05).
Conclusion: Our findings suggest that the posterolateral approach is an alternative method for TFESI in cases where needle tip positioning in the anterior epidural space is difficult.
Figures
References
-
- Botwin KP, Gruber RD, Bouchlas CG, et al. Fluoroscopically guided lumbar transforaminal epidural steroid injections in degenerative lumbar stenosis. Am J Phys Med Rehabil 2002;81:898–905 - PubMed
-
- Slipman CW, Chow DW. Therapeutic spinal corticosteroid injections for the management of radiculopathies. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am 2002;13:697–711 - PubMed
-
- Vad VB, Bhat AL, Lutz GE, et al. Transforaminal epidural steroid injections in lumbosacral radiculopathy: a prospective randomized study. Spine 2002;27:11–15 - PubMed
-
- Husemeyer RP, White DC. Topography of the lumbar epidural space. A study in cadavers using injected polyester resin. Anaesthesia 1980;35:7–11 - PubMed
-
- Bogduk N, Aprill C, Derby R. Epidural spinal injections. In: White AH, Schollerman J, eds. Spinal Care: Diagnosis and Treatment. St Louis: Mosby,1995. :322–43
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
