Angiographic follow-up of traumatic carotid cavernous fistulas treated with endovascular stent graft placement
- PMID: 17297009
- PMCID: PMC7977413
Angiographic follow-up of traumatic carotid cavernous fistulas treated with endovascular stent graft placement
Abstract
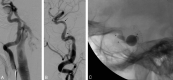
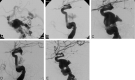
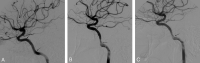
Background and purpose: Endovascular treatment (EVT) of carotid cavernous fistulas (CCFs) is based on various techniques, mainly those using detachable balloons. Coronary covered stent grafts have been sporadically used in the intracranial arteries and only 2 traumatic CCFs have been reported in the literature; moreover, there is poor information about the long-term follow-up. We present 8 cases of CCFs treated by the placement of a covered stent, 5 of which have a 1-year clinical and angiographic follow-up.
Methods: Eight patients with posttraumatic CCF were treated by positioning a covered stent in the intracranial internal carotid artery (ICA) to occlude the fistula. They received periodic clinical and angiographic follow-up to evaluate the patency and the stability of clinical results.
Results: In all cases, the symptoms related to the CCF regressed after treatment and did not recur in the follow-up. Two patients presented residual filling of the CCF at the end of the procedure. The angiographic follow-up revealed in 6 patients of 7 a good patency of the ICA; in 1 patient, there was an ICA asymptomatic occlusion. One patient required transvenous coil occlusion of the cavernous sinus.
Conclusion: When standard treatments fail, covered stent grafts can be used as a valid alternative in the treatment of CCFs, but more data are needed, especially in the long-term follow-up.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Carotid cavernous fistulas treated by endovascular covered stent grafts with follow-up results.Br J Neurosurg. 2010 Aug;24(4):435-40. doi: 10.3109/02688697.2010.487127. Br J Neurosurg. 2010. PMID: 20515263 Review.
-
Endovascular treatment of posttraumatic carotid-cavernous fistulas and pseudoaneurysms with covered stents.J Neuroimaging. 2014 May-Jun;24(3):287-91. doi: 10.1111/jon.12023. Epub 2013 Apr 26. J Neuroimaging. 2014. PMID: 23621764 Clinical Trial.
-
The evolution of endovascular treatment of carotid cavernous fistulas: a single-center experience.World Neurosurg. 2013 Nov;80(5):538-48. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2013.02.033. Epub 2013 Feb 9. World Neurosurg. 2013. PMID: 23402868
-
Placement of covered stents for the treatment of direct carotid cavernous fistulas.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2009 Aug;30(7):1342-6. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A1583. Epub 2009 Apr 2. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2009. PMID: 19342540 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Endovascular techniques for treatment of carotid-cavernous fistula.J Neuroophthalmol. 2009 Mar;29(1):62-71. doi: 10.1097/WNO.0b013e3181989fc0. J Neuroophthalmol. 2009. PMID: 19458580 Review.
Cited by
-
Treatment of direct carotid-cavernous fistula with Willis covered stent with midterm follow-up.Chin Neurosurg J. 2021 Sep 13;7(1):41. doi: 10.1186/s41016-021-00256-y. Chin Neurosurg J. 2021. PMID: 34517922 Free PMC article.
-
Contemporary Strategies in the Management of Civilian Neck Zone II Vascular Trauma.Front Surg. 2017 Sep 29;4:56. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2017.00056. eCollection 2017. Front Surg. 2017. PMID: 29034244 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coil embolization of cavernous sinus in patients with direct and dural arteriovenous fistula.Eur Radiol. 2009 Jun;19(6):1443-9. doi: 10.1007/s00330-008-1278-1. Epub 2009 Jan 10. Eur Radiol. 2009. PMID: 19137301 Clinical Trial.
-
Transarterial and Transvenous Coil Embolization of Direct Carotid-Cavernous Fistulas.J Neuroendovasc Ther. 2022;16(2):127-134. doi: 10.5797/jnet.tn.2020-0115. Epub 2021 May 27. J Neuroendovasc Ther. 2022. PMID: 37502641 Free PMC article.
-
First line Treatment of Traumatic Carotid Cavernous Fistulas Using Covered Stents at Level 1 Regional Trauma Center.J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2021 Sep;64(5):818-826. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2020.0345. Epub 2021 Jul 23. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2021. PMID: 34293848 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barrow DL, Spector RH, Braun IF, et al. Classification and treatment of spontaneous carotid-cavernous sinus fistulas. J Neurosurg 1985;62:248–56 - PubMed
-
- Hoops JP, Rudolph G, Schriever S, et al. [Dural carotid-cavernous sinus fistulas: clinical aspects, diagnosis and therapeutic intervention]. Klin Monatsbl Augenheilkd 1997;210:392–97 - PubMed
-
- Lemaitre J, Jamart S, Lefranc F, et al. [Post-traumatic carotid-cavernous sinus fistula]. Rev Med Brux 1999;20:91–94 - PubMed
-
- Chuman H, Trobe JD, Petty EM, et al. Spontaneous direct carotid-cavernous fistula in Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type IV: two case reports and a review of the literature. J Neuroophthalmol 2002;22:75–81 - PubMed
-
- Fages-Caravaca EM, Tembl-Ferrairo JI, Lago-Martin A, et al. [Direct carotid cavernous fistulas: endovascular treatment using a detachable balloon]. Rev Neurol 2001;33:533–36 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
