Relationship of serum adiponectin and resistin levels with breast cancer risk
- PMID: 17297263
- PMCID: PMC2693546
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2007.22.1.117
Relationship of serum adiponectin and resistin levels with breast cancer risk
Abstract
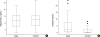
Obesity is one of the well-known risk factors of breast cancer. We evaluated the relationship between serum adiponectin and resistin levels and breast cancer risk in 41 biopsy-proven breast cancer patients and 43 age- and body mass index-matched controls. The mean serum adiponectin level was lower in the breast cancer group than the control group (6.93+/-3.2 microg/mL, vs. 7.60+/-3.5 microg/mL), but this difference did not reach statistical significance (p=0.37). There was a statistically significant difference in serum resistin levels between the groups (breast cancer group 5.23+/-6.9 ng/mL vs. control 1.46+/-2.0 ng/mL; p<0.001). The risk of breast cancer was significantly increased in the highest tertile group for serum resistin level compared to the lowest tertile group (adjusted odds ratio 2.77 [95% CI 1.40-5.50]). The lymph node metastasis was significantly increased in the patients with less than the median adiponectin level (p=0.017). In the patients whose resistin level was higher than the median, the frequency of tumor with the highest histological grade was significantly increased (p=0.025). In conclusions, both the low serum adiponectin levels and high resistin levels are likely to be associated with increased breast cancer risk in Korean women.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Adipocytokines and breast cancer risk.Chin Med J (Engl). 2007 Sep 20;120(18):1592-6. Chin Med J (Engl). 2007. PMID: 17908478
-
The relationship between serum adiponectin and resistin levels, insulin resistance and colorectal adenomas.Turk J Gastroenterol. 2015 Jan;26(1):20-4. doi: 10.5152/tjg.2015.3626. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 25698266
-
Resistin, visfatin, adiponectin, and leptin: risk of breast cancer in pre- and postmenopausal saudi females and their possible diagnostic and predictive implications as novel biomarkers.Dis Markers. 2015;2015:253519. doi: 10.1155/2015/253519. Epub 2015 Mar 8. Dis Markers. 2015. PMID: 25838618 Free PMC article.
-
Equol, adiponectin, insulin levels and risk of breast cancer.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013;14(4):2191-9. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2013.14.4.2191. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013. PMID: 23725111 Review.
-
Serum adiponectin in breast cancer: A meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Jul;97(29):e11433. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000011433. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 30024516 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hyperresistinemia in Obese Female Dogs With Mammary Carcinoma in Benign-Mixed Tumors and Its Correlation With Tumor Aggressiveness and Survival.Front Vet Sci. 2020 Aug 13;7:509. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2020.00509. eCollection 2020. Front Vet Sci. 2020. PMID: 32903534 Free PMC article.
-
Resistin, a fat-derived secretory factor, promotes metastasis of MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells through ERM activation.Sci Rep. 2016 Jan 5;6:18923. doi: 10.1038/srep18923. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26729407 Free PMC article.
-
Adiponectin and leptin molecular actions and clinical significance in breast cancer.Int J Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Res. 2014;8(1):31-40. Int J Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Res. 2014. PMID: 24505549 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum irisin levels are lower in patients with breast cancer: association with disease diagnosis and tumor characteristics.BMC Cancer. 2015 Nov 11;15:898. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1898-1. BMC Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26560078 Free PMC article.
-
Screening for Multiple Autoantibodies in Plasma of Patients with Breast Cancer.Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2017 Nov-Dec;14(6):427-435. doi: 10.21873/cgp.20052. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2017. PMID: 29109092 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Harvie M, Hooper L, Howell AH. Central obesity and breast cancer risk: a systematic review. Obes Rev. 2003;4:157–173. - PubMed
-
- Newman SC, Lees AW, Jenkins HJ. The effect of body mass index and oestrogen receptor level on survival of breast cancer patients. Int J Epidemiol. 1997;26:484–490. - PubMed
-
- Edman CD, Aiman EJ, Porter JC, MacDonald PC. Identification of the estrogen product of extraglandular aromatization of plasma androstenedion. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1978;130:439–447. - PubMed
-
- Verkasalo PK, Thomas HV, Appleby PN, Davey GK, Key TJ. Circulating levels of sex hormones and their relation to risk factors for breast cancer: a cross-sectional study in 1092 pre and postmenopausal women. Cancer Causes Control. 2001;12:47–59. - PubMed
-
- Hankinson SE, Wilett WC, Manson JE, Colditz GA, Hunter DJ, Speigelman D, Barbieri RL, Spiezer FE. Plasma sex steroid hormone levels and risk of breast cancer in postmenopausal women. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1998;90:1292–1299. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical