Neuroprotective effects of growth hormone against hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in neonatal rats: 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopic study
- PMID: 17297264
- PMCID: PMC2693548
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2007.22.1.122
Neuroprotective effects of growth hormone against hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in neonatal rats: 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopic study
Abstract
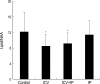
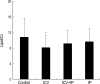
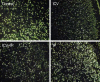
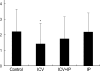
Using 1H-MRS, we evaluated the effects of growth hormone (GH) as a caspase inhibitor on hypoxic-ischemic injury in neonatal rat brains. The right common carotid arteries of rats were ligated, allowed to recover for 3 hr, and exposed to 8% oxygen for 2 hr. GH was given just prior to HI insult and animals were divided into four groups: control, intracerebroventricular (ICV), intracerebroventricular/intraperitoneal (ICV/IP), and intraperitoneal (IP). Localized in vivo 1H-MRS and TUNEL staining were performed 24 hr after HI injury. Lipid/N-acetyl aspartate (NAA) and lipid/creatine (Cr) ratios were used as apoptotic markers. Gross morphologic changes at 2 weeks were used to evaluate the effects of GH. The lipid/NAA ratio was lower in the ICV and ICV/IP groups than in the control, and the lipid/Cr ratio was lower in the ICV group than in the control. The number of TUNEL positive cells was decreased in the ICV and ICV/IP groups, and the degree of morphologic change indicative of brain injury was lower in the ICV group and somewhat lower in the ICV/IP group. The degree of morphologic change correlated with the lipid/NAA and lipid/Cr ratios. These findings suggest that GH exerts neuroprotective effects in cerebral hypoxic-ischemic injury.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Similar neuroprotective effects of ischemic and hypoxic preconditioning on hypoxia-ischemia in the neonatal rat: a proton MRS study.Int J Dev Neurosci. 2013 Nov;31(7):616-23. doi: 10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2013.08.001. Epub 2013 Aug 16. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23958850
-
The effects of dantrolene on hypoxic-ischemic injury in the neonatal rat brain.Anesth Analg. 2008 Jan;106(1):227-33, table of contents. doi: 10.1213/01.ane.0000287663.81050.38. Anesth Analg. 2008. PMID: 18165582
-
Protective effect of hypoxic preconditioning on hypoxic-ischemic injured newborn rats.J Korean Med Sci. 2011 Nov;26(11):1495-500. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2011.26.11.1495. Epub 2011 Oct 27. J Korean Med Sci. 2011. PMID: 22065907 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective effect of the peptides ADNF-9 and NAP on hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in neonatal rats.Brain Res. 2006 Oct 18;1115(1):169-78. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2006.07.114. Epub 2006 Aug 30. Brain Res. 2006. PMID: 16938277
-
Neuroprotective effects of lithium treatment following hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in neonatal rats.Childs Nerv Syst. 2012 Feb;28(2):191-8. doi: 10.1007/s00381-011-1627-2. Epub 2011 Nov 18. Childs Nerv Syst. 2012. PMID: 22094358
Cited by
-
Growth Hormone (GH) Enhances Endogenous Mechanisms of Neuroprotection and Neuroplasticity after Oxygen and Glucose Deprivation Injury (OGD) and Reoxygenation (OGD/R) in Chicken Hippocampal Cell Cultures.Neural Plast. 2021 Sep 16;2021:9990166. doi: 10.1155/2021/9990166. eCollection 2021. Neural Plast. 2021. PMID: 34567109 Free PMC article.
-
GH mediates exercise-dependent activation of SVZ neural precursor cells in aged mice.PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e49912. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0049912. Epub 2012 Nov 27. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23209615 Free PMC article.
-
Growth Hormone (GH) Crosses the Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB) and Induces Neuroprotective Effects in the Embryonic Chicken Cerebellum after a Hypoxic Injury.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 30;23(19):11546. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911546. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36232848 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective Effects of Growth Hormone (GH) and Insulin-Like Growth Factor Type 1 (IGF-1) after Hypoxic-Ischemic Injury in Chicken Cerebellar Cell Cultures.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 29;22(1):256. doi: 10.3390/ijms22010256. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33383827 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vannucci RC. Current and potentially new management strategies for perinatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Pediatrics. 1990;85:961–968. - PubMed
-
- Holshouser BA, Ashwal S, Luh GY, Shu S, Kahlon S, Auld KL, Tomasi LG, Perkin RM, Hinshaw DB., Jr Proton MR spectroscopy after acute central nervous system injury: outcome prediction in neonates, infants, and children. Radiology. 1997;202:487–496. - PubMed
-
- Novotny E, Ashwal S, Shevell M. Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy: An emerging technology in pediatric neurology research. Pediatr Res. 1998;44:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Peden CJ, Cowan FM, Bryant DJ, Sargentoni J, Cox IJ, Menon DK, Gadian DG, Bell JD, Dubowitz LM. Proton MR spectroscopy of the brain in infants. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1990;14:886–894. - PubMed
-
- Shu SK, Ashwal S, Holshouser BA, Nystrom G, Hinshaw DB., Jr Prognostic value of 1H-MRS in perinatal CNS insults. Pediatr Neurol. 1997;17:309–318. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

