Quinone-induced enhancement of DNA cleavage by human topoisomerase IIalpha: adduction of cysteine residues 392 and 405
- PMID: 17298034
- PMCID: PMC2896225
- DOI: 10.1021/bi062017l
Quinone-induced enhancement of DNA cleavage by human topoisomerase IIalpha: adduction of cysteine residues 392 and 405
Abstract
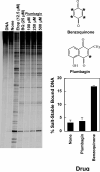
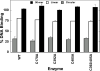
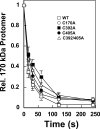
Several quinone-based metabolites of drugs and environmental toxins are potent topoisomerase II poisons. These compounds act by adducting the protein and appear to increase levels of enzyme-DNA cleavage complexes by at least two potentially independent mechanisms. Treatment of topoisomerase IIalpha with quinones inhibits DNA religation and blocks the N-terminal gate of the protein by cross-linking its two protomer subunits. It is not known whether these two effects result from adduction of quinone to the same amino acid residue(s) in topoisomerase IIalpha or whether they are mediated by modification of separate residues. Therefore, this study identified amino acid residues in human topoisomerase IIalpha that are modified by quinones and determined their role in the actions of these compounds as topoisomerase II poisons. Four cysteine residues were identified by mass spectrometry as sites of quinone adduction: Cys170, Cys392, Cys405, and Cys455. Mutations (Cys --> Ala) were individually generated at each position. Only mutations at Cys392 or Cys405 reduced sensitivity ( approximately 50% resistance) to benzoquinone. Top2alphaC392A and top2alphaC405A displayed faster rates ( approximately 2-fold) of DNA religation than wild-type topoisomerase IIalpha in the presence of the quinone. In contrast, as determined by DNA binding, protein clamp closing, and protomer cross-linking experiments, mutations at Cys392 and Cys405 did not affect the ability of benzoquinone to block the N-terminal gate of topoisomerase IIalpha. These findings indicate that adduction of Cys392 and Cys405 is important for the actions of quinones against the enzyme and increases levels of cleavage complexes primarily by inhibiting DNA religation.
Figures




References
-
- Wang JC. DNA Topoisomerases. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1996;65:635–692. - PubMed
-
- Nitiss JL. Investigating the biological functions of DNA topoisomerases in eukaryotic cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1998;1400:63–81. - PubMed
-
- Wang JC. Moving one DNA double helix through another by a type II DNA topoismerase: the story of a simple molecular machine. Quart. Rev. Biophys. 1998;31:107–144. - PubMed
-
- Fortune JM, Osheroff N. Topoisomerase II as a target for anticancer drugs: when enzymes stop being nice. Prog. Nucleic Acid. Res. Mol. Biol. 2000;64:221–253. - PubMed
-
- Champoux JJ. DNA topoisomerases: structure, function, and mechanism. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2001;70:369–413. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

